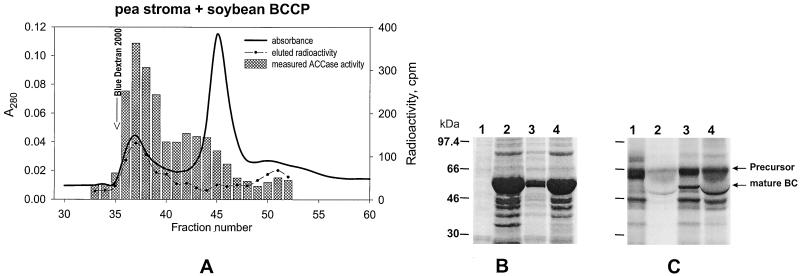
Figure 4.
A, Coelution of pea ACCase and [3H]BCCP. [3H]BCCP precursors were synthesized in vitro and imported into isolated pea chloroplasts. Plastid ACCase activity in the stromal fractions was determined after chromatography with a Sephacryl S300 column. Identical results obtained with α-CT precursors produced from accA were used in the same type of experiment (Reverdatto et al., 1997). B and C, Processing of the in vitro-synthesized soybean BC precursor by pea chloroplasts. Lanes 1, Translation with [35S]Met. Lanes 2, Intact pea chloroplasts incubated with the BC precursor and reisolated through a Percoll cushion (total chloroplast protein). Lanes 3, BC precursor incubated with pea stromal preparation that has CPE activity. Lanes 4, Same as for lanes 3, but 5× concentrated (by ultrafiltration through Microcon-30) pea stroma. Note that lanes 2 and 4 contain sizable amounts of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, which causes the band attributable to mature BC to be distorted, whereas in lanes 3 there is no distortion. B, Coomassie blue stain for total protein. C, Autoradiogram of the gel from B. These data show that the soybean BC precursors processed after import into chloroplasts, and by cleavage with CPE, are of the same apparent size.