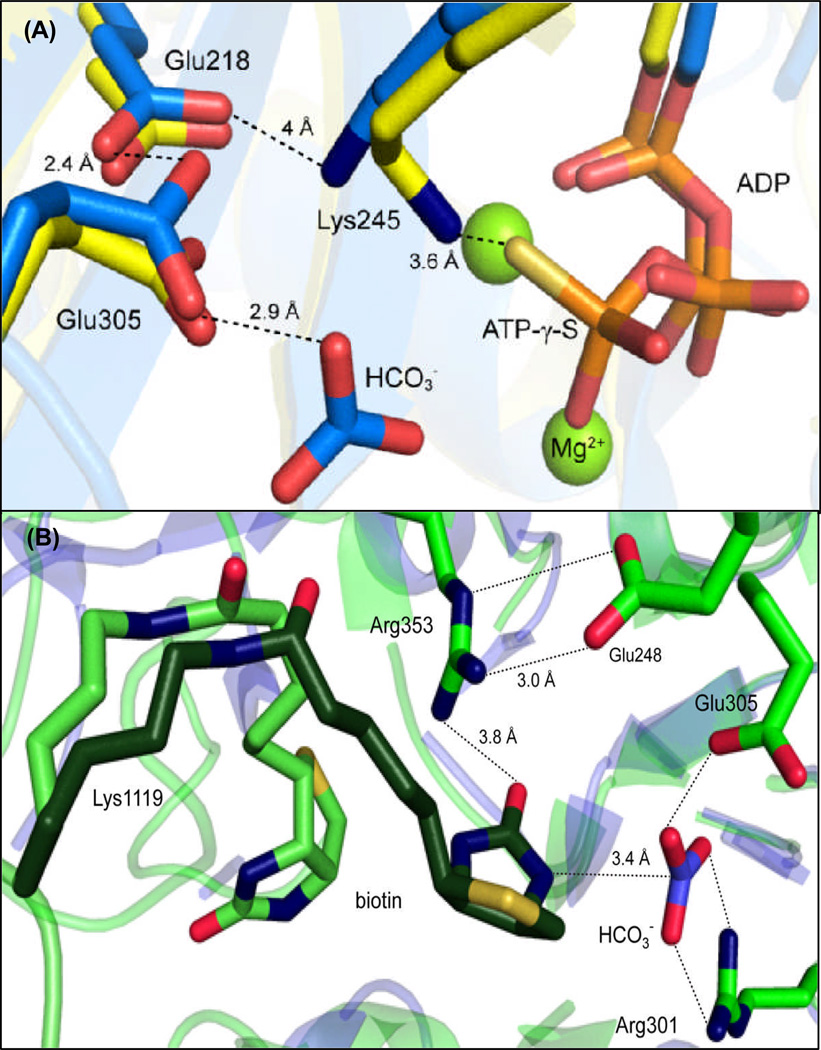
Figure 4.
(A) Hydrogen-bonding interactions of the highly conserved catalytic triad, Glu218-Lys245-Glu305, HCO3− and MgATP-γ-S determined from the superposition of EcBC (blue, 8) and RePC holoenzyme (yellow, 3). The position of Glu218 in both the RePC and EcBC structures suggest that its main catalytic function is to position Lys245 and lower the pKa of Glu305. (B) The actual (light green) and modeled (dark green) positions of tethered biotin in the BC domain active site of the T882A RePC mutant crystal structure (pdb 3WT6) relative to the positioning of HCO3− in the BC domain active site from EcBC (blue). Hydrogen bonding interactions between key residues are indicated by dashed lines.