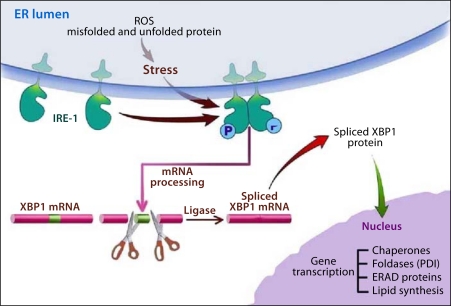
Fig. 1.
ER stress with alcohol abuse and the adaptive UPR. Alcohol metabolism causes increased ROS leading to unfolded and misfolded nascent proteins in the ER. The ER stress also results in activation of an adaptive UPR led by activation of IRE-1 through homodimerization. Activated IRE-1 is an RNAse directed to splicing out in intron of XBP1 leading to XBP1-S mRNA. XBP1-S is translated into a potent transcription factor that regulates the expression of chaperones, foldases including PDI, components of the ERAD system and enzymes of lipid synthesis needed to expand the ER. These effects adapt the ER to the ER stress caused by alcohol abuse.