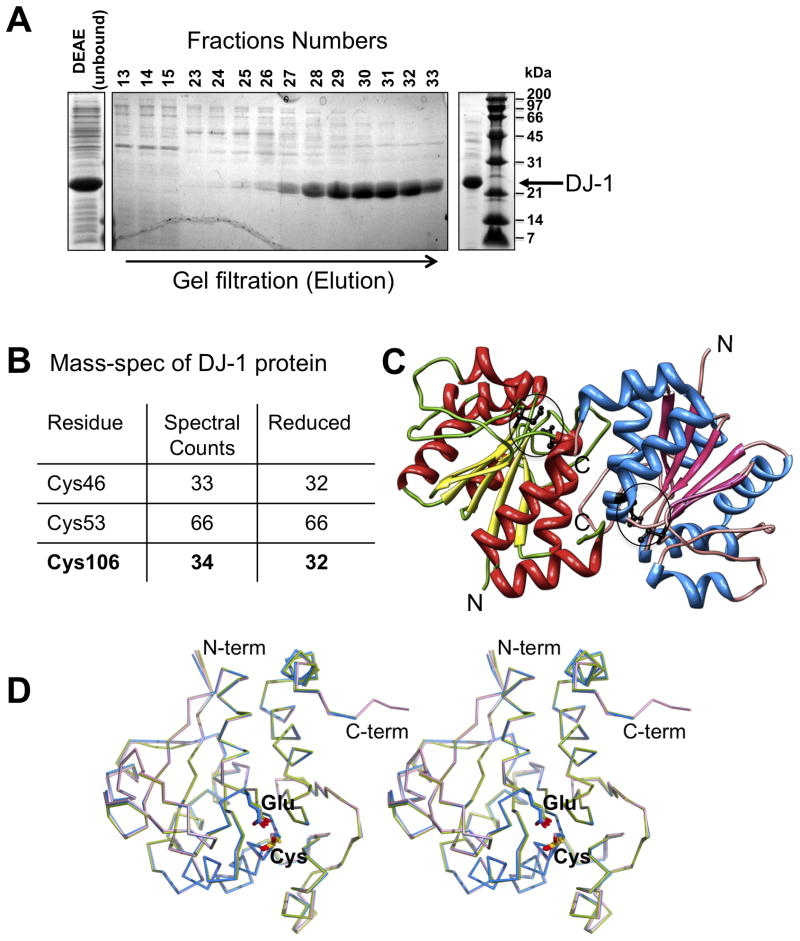
Figure 1. Purification and crystal structure of DJ-1.
A. Purification of reduced DJ-1 at pH 5.0 visualized by SDS-PAGE depicting crude extract (left), gel filtration elution profile (middle) and the DJ-1 preparation used for MS analysis and crystallization (right). B. MS analysis depicting reduced DJ-1. The total number of spectral counts for peptides containing assigned cysteines (“residues”) is displayed as well as the number of these counts referring to alkylated cysteines in these peptides indicating reactive (”reduced”) state of the cysteines. C. Overall structure of the asymmetric unit. The two independent copies of DJ-1 observed in the crystallographic asymmetric unit forming the characteristic DJ-1 dimer are colored separately, with the location of Cys106 and Glu18 indicated by circles D. Structural comparison of DJ-1 in different oxidation states. Structural overlay of two independent copies of DJ-1 reported here showing molecule 1 (with reduced Cys106; blue), molecule 2 (with mono-oxygenized Cys106; magenta) along with a DJ-1 structure determined previously in which Cys106 is oxidized to its sulfinic acid form (green; PDB Id: 1SOA).