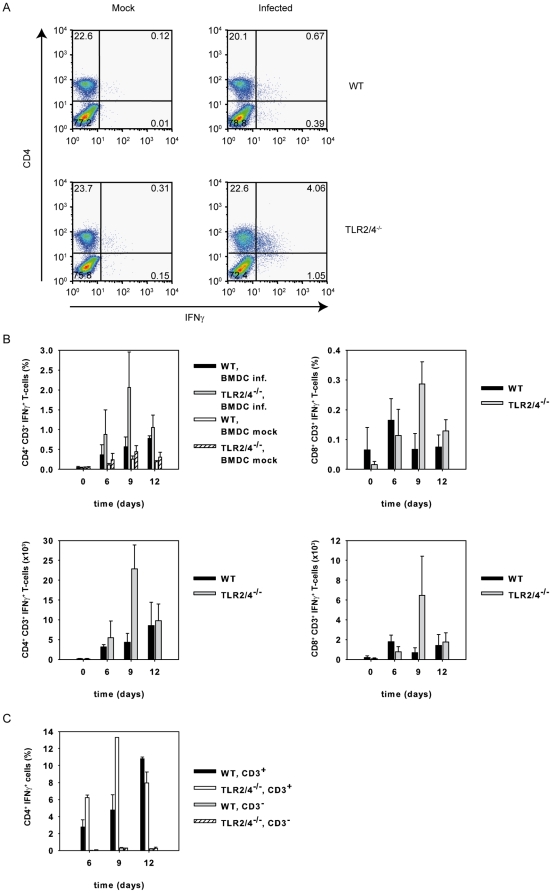
Figure 3. C. pneumoniae-specific CD4+ T cells are responsible for the enhanced IFNγ-response in TLR2/4 double-deficient mice.
(A) Pulmonary cells were prepared from wild type and TLR2/4 double-deficient mice nine days post infection with C. pneumoniae. The cells (1×105 cells/well) were then re-stimulated with BMDC (1×105 cells/well) which were or were not infected with C. pneumoniae (MOI = 5). After 1 h of culture Brefeldin A was added, the culture continued for another 12 h and cells were stained for CD4, CD8 and intracellular IFNγ. FACS graphs show the IFNγ response of CD4+ T-cells. (B) Pulmonary cells from C. pneumoniae-infected wild type (n = 3/time point) and TLR2/4 (n = 3/time point) double-deficient mice were prepared at different time points as indicated in the graph. Mock infected animals served as controls (time point 0). Cells were stained with mAbs specific for CD3, CD4, CD8 and IFNγ as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed by flow cytometry. Upper graphs show frequncies, lower graphs absolute numbers of IFNγ+CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. (C) Pulmonary cells were prepared from C. pneumoniae-infected wild type (n = 2/time point) of TLR2/4 double-deficient mice (n = 2 6d, n = 1 9d, n = 12d) after 6, 9, and 12 days post infection and the cells were stained for CD4, CD3 and IFNγ. Note that CD4+CD3− cells hardly contribute to IFNγ-secretion.