Figure 3.
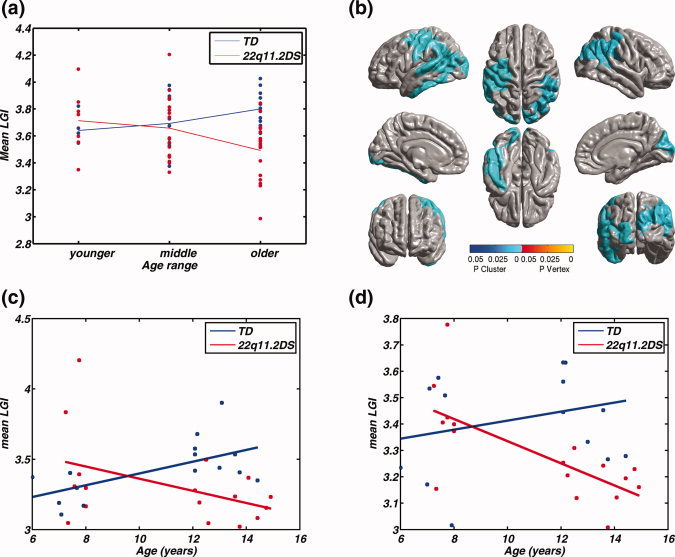
(a) Main effect of age showing the mean lGI in the cluster in Figure 2b, split by diagnosis and age ranges of younger (6–9 years), middle (9–12 years) and older (12–15 years). Visually, the mean lGI changes differently across diagnosis groups, and across age ranges for children with 22q11.2DS, the mean lGI reduces by a greater amount between the middle and older group, when compared with that between younger and middle group. (b) Clusters showing significant interaction between age ranges and diagnosis, where the levels of age were from the younger and the older age range. The cortical areas showing opposite patterns of age‐related changes in cortical gyrification in TD children and in children 22q11.2DS are spread across both the hemispheres. The parietal aspect of the cortex is involved bilaterally. The left hemisphere cluster also includes the superior/inferior temporal regions, whereas the right hemisphere includes the cuneus, among other regions, in which the lGI decreased significantly in the children with the deletion, when compared with the typical controls. (b) Plot of the mean lGI values in the left cluster as a function of age (F(1,28) = 9.01, P = 0.006), (c) Plot of the mean lGI values in the right cluster as a function of age (F(1,28) = 8.39, P = 0.007). MNI coordinates and other descriptive statistics have been tabulated in Table III.
