Fig. 2.
Absence of extracellular nucleases results in alterations of the biofilm architecture.
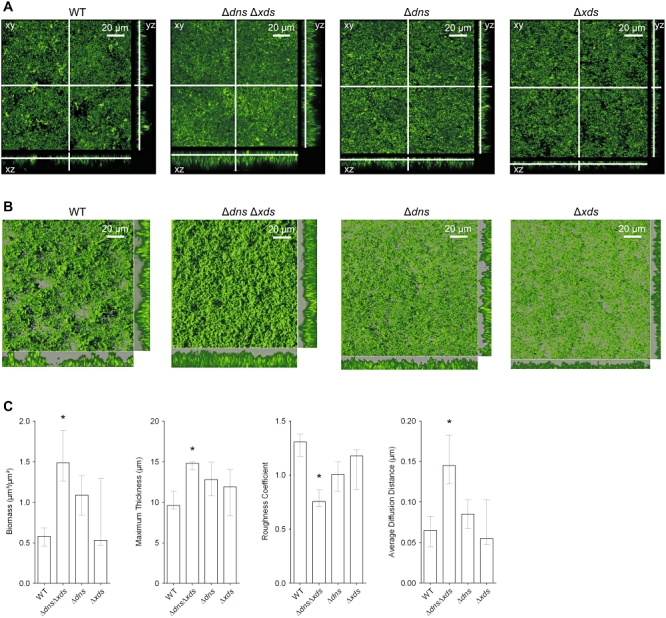
A. Shown are confocal laser scanning microscopy images of the wild type, ΔdnsΔxds, Δdns and Δxds mutant biofilms as horizontal (xy) and vertical (xz and yz) projections (large and side panels, respectively). Biofilms were allowed to form for 9 h in flow cell chambers supplied with LB and stained with SYTO 9 fluorescent nucleic acid stain. Large panels represent selected single optical sections through the acquired three-dimensional data sets.
B. Micrographs represent three-dimensional images of the wild type, ΔdnsΔxds, Δdns and Δxds mutant biofilms analysed by the IMARIS software package using same data sets as in panel (A). The large images are three-dimensional top-down images of the biofilms, and the small images to the right of and below the large images are side views of sections. Movies of the wild type and ΔdnsΔxds mutant biofilms, which allow views from different angles, are provided in the supporting information (bf_wt.mov and bf_mut.mov).
C. Image stacks of the wild type and mutant biofilms were analysed for the biomass, the maximum thickness, the roughness coefficient and the average diffusion distance using the COMSTAT software. Shown are the medians of at least six image stacks from three independent experiments for each strain. The error bars indicate the interquartile range. Significant differences (*P < 0.05) of structural parameters are indicated for the multiple comparisons of the deletion mutants with the wild type.
