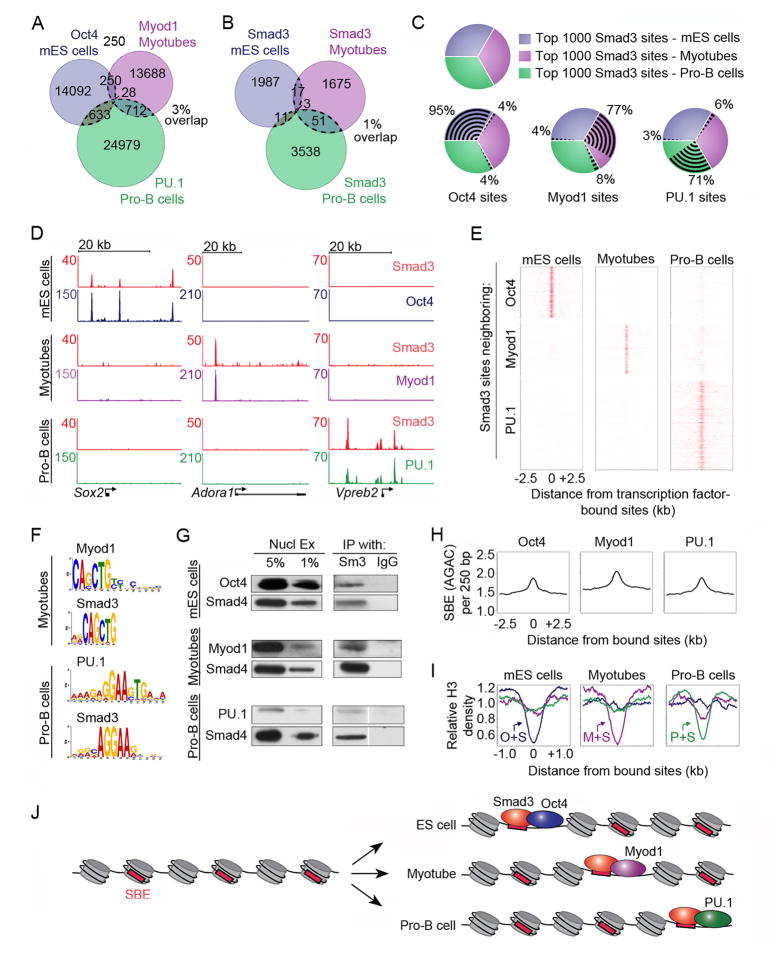
Figure 4. Smad3 co-occupies DNA with cell-type-specific master transcription factors.
(A) Master transcription factors bind unique sites in different cell types. The Venn diagram shows the overlap of sites bound by Oct4 in mES cells (blue), Myod1 in myotubes (purple) and PU.1 in pro-B cells (green) (Table S1). The total number of bound sites is indicated for each shaded area. 3% of all sites overlap in at least two cell types (indicated by dotted lines).
(B) Smad3 binds unique sites in different cell types. The Venn diagram shows the overlap of Smad3-bound regions between mES cells (blue), myotubes (purple) and pro-B cells (green). 1% of Smad3-bound sites overlap in at least two cell types. Myotubes and Pro-B cells were treated with TGF-β prior to analysis of Smad3 binding.
(C) Smad3 co-occupies sites with master transcription factors that are cell-type specific. The 1000 strongest Smad3 binding sites (by peak height) were chosen from each cell type for analysis (top left). The co-occupancy of Oct4 (bottom left), Myod1 (bottom center) and PU.1 (bottom right) with Smad3 in each cell type is shown.
(D) Smad3 co-occupies cell-type-specific sites with master transcription factors at individual genes. Gene tracks represent binding of Smad3 and Oct4 in mES cells (top), Smad3 and Myod1 in myotubes (center) and Smad3 and PU.1 in pro-B cells (bottom) for the genes encoding Sox2, Adora1 and Vpreb2. The floor is set at 3 counts. See also Figure S3.
(E) Smad3 co-occupies the genome with cell-type-specific master transcription factors. Binding plots show the location of Smad3-bound sites in mES cells (left), myotubes (center) and pro-B cells (right) relative to sites bound by Oct4 in mES cells (top), Myod1 in myotubes (middle) and PU.1 in pro-B cells (bottom).
(F) Smad3 binding sites are enriched for the motif of the cell-type-specific master transcription factor. Motif discovery was performed using Myod1 and Smad3-bound sites identified in myotubes (top) and PU.1 and Smad3-bound sites in pro-B cells (bottom). The most enriched motifs are shown.
(G) Smad3 interacts with master transcription factors. Co-IPs with antibodies against Smad3 (Sm3) and IgG were performed using nuclear lysates from mES cells (top), myotubes (center), and pro-B cells (bottom). Precipitated complexes were probed for Oct4 in mES cells, Myod1 in myotubes and PU.1 in pro-B cells. Smad4 was used as a positive control for immunoprecipitation.
(H) SBEs are enriched at sites occupied by master transcription factors. The average frequency of SBEs in a 250 bp window across a 5kb region centered on the binding site of each transcription factor is indicated.
(I) Nucleosomes are depleted at sites co-occupied by Smad3 and master transcription factors. Relative H3 density centered on sites co-occupied by Oct4 and Smad3 (O+S) in mES cells (left), Myod1 and Smad3 (M+S) in myotubes (center) and PU.1 and Smad3 (P+S) in pro-B cells (right) is shown.
(J) Model for cell-type specific genome occupancy by Smad3. Cell-type specific Smad3 binding may be determined by interactions with master transcription factors, which occupy nucleosome-depleted regions and recruit Smad3 to cell-type-specific sites. Red boxes indicate SBEs and gray cylinders represent nucleosomes.