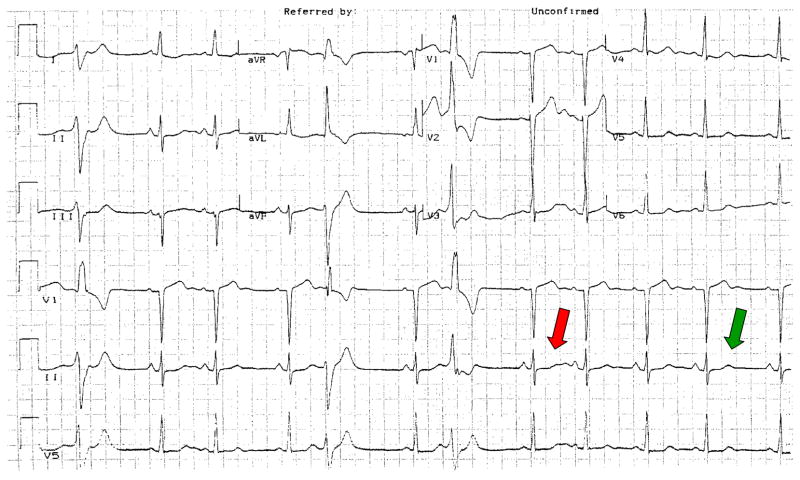
Figure 1.
Which QT predicts arrhythmias? The complex indicated by the green arrow is at steady state, and normal. However, the complex indicated in red, which follows a pause, displays grotesque deformity. This example reinforces the concept that the answer to the “controversy” of whether the QT should be retained or jettisoned as an indicator of arrhythmias depends on what we now know – and what we need to learn – about its physiology and pathophysiology: discarding the QT as a measure of arrhythmia susceptibility in his case because the steady state QT is normal would be a mistake.