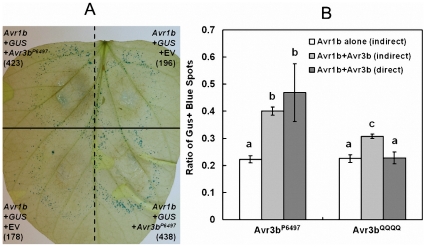
Figure 7. Avr3b suppresses ETI triggered by P. sojae effector Avr1b.
Suppression of Avr1b-triggered PCD in soybean cultivar L77–1863 (Rps1b) by Avr3bP6497 and Avr3bQQQQ measured by indirect and direct double barrel particle bombardment assays. (A) Side-by-side comparison of cell death triggered by co-bombardment of Avr1b alone compared to Avr1b+Avr3bP6497 on Rps1b soybean. Numbers in parenthesis indicate total GUS positive spots counted for each treatment on the leaf shown. Co-bombardments occur horizontally and are separated by dashed lines. Replicate bombardments are separated by the solid black line. (B) Quantitation of suppression by indirect and direct co-bomardment assays. For the indirect assay the number of GUS-expressing spots surviving in the presence of Avr1b on Rps1b soybean, was measured relative to a parallel GUS-only control in the presence (light grey bars) or absence (white bars) of Avr3bP6497 or Avr3bQQQQ. For the direct assay (dark gray bars) one barrel delivered DNA encoding Avr1b + Avr3bP6497 or Avr3bQQQQ and the other barrel delivered Avr1b DNA only. The direct ratio was then multiplied by the cell survival in the presence of Avr1b alone on Rps1b Soybean (white bars) to enable comparison to the results of the indirect assays. Based on the Wilcoxon signed ranks test (direct assays) or the Wilcoxon rank sum test (indirect assays and comparisons of two direct assays), outcomes that were significantly different p <0.001 are marked with different letters.