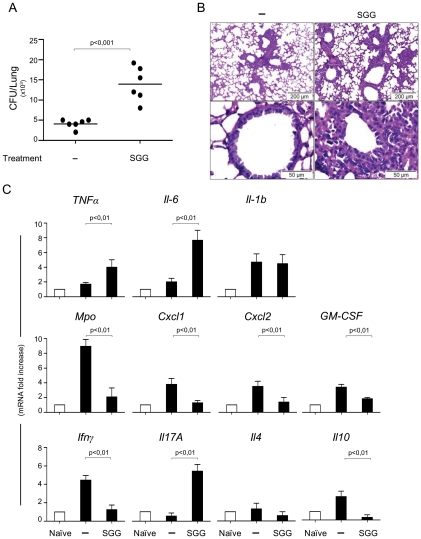
Figure 5. Impact of SGG on primary aspergillosis in intact mice.
A, C57BL/6 mice were first injected with SGG at day 3, 2 and 1 before conidial inhalation and infected on day 0 with 2×107 Aspergillus conidia. Naïve are uninfected mice, – are infected, untreated mice and SGG are mice that have received SGG (250 mg/kg i.n. the day of the infection and on days 1, 2 and 3 post-infection). Fungal growth is expressed as CFUs per lung and statistical significance is indicated by a p value <0.001. Results pooled from 2 experiments (6 animals/group) with one example shown in panel A. B, Lung histology (PAS-staining) of mice treated as indicated, 3 days after infection showing signs of inflammatory pathology in the immunocompetent mice treated with SGG. C, Cytokines were determined by RT-PCR in lung homogenates 3 days after the infection. Note that SGG induced inflammatory cytokine gene expression, such as Tnfα, Il6, Il17a and Il4 genes, but suppressed Ifnγ and Il10 expression; the low level of Mpo gene expression is in agreement with the low counts of neutrophils in the lung of infected mice. Bars indicate SEM and statistical significance is indicated by p values.