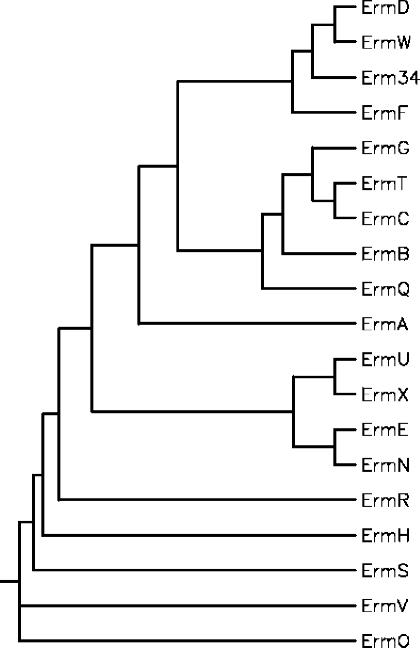
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic relationships among Erm methylases. The tree was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method. Sequences are from S. aureus [Erm(A) (accession no. X03216) and Erm(C) (accession no. J01755)], Streptococcus pneumoniae [Erm(B) (accession no. X52632)], B. licheniformis [Erm(D) (accession no. M29832)], Saccharopolyspora erythraea [Erm(E) (accession no. X51891)], Bacteroides fragilis [Erm(F) (accession no. M14730)], B. sphaericus [Erm(G) (accession no. M15332)], Streptomyces thermotolerans [Erm(H) (accession no. P13079)], Streptomyces fradiae [Erm(N) (accession no. X97721) and [Erm(S)], Streptomyces lividans [Erm(O) (accession no. M74717)], Clostridium perfringens [Erm(R) (accession no. L22689)], Arthrobacter sp. [Erm(R) (accession no. M11276)], Lactobacillus reuteri [Erm(T) (accession no. M64090)], Streptomyces lincolnensis [Erm(U) (accession no. X62867)], Corynebacterium diphtheriae [Erm(X) (accession no. M36726)], M. griseorubida [Erm(W) (accession no. D14532)], and B. clausii [Erm34].