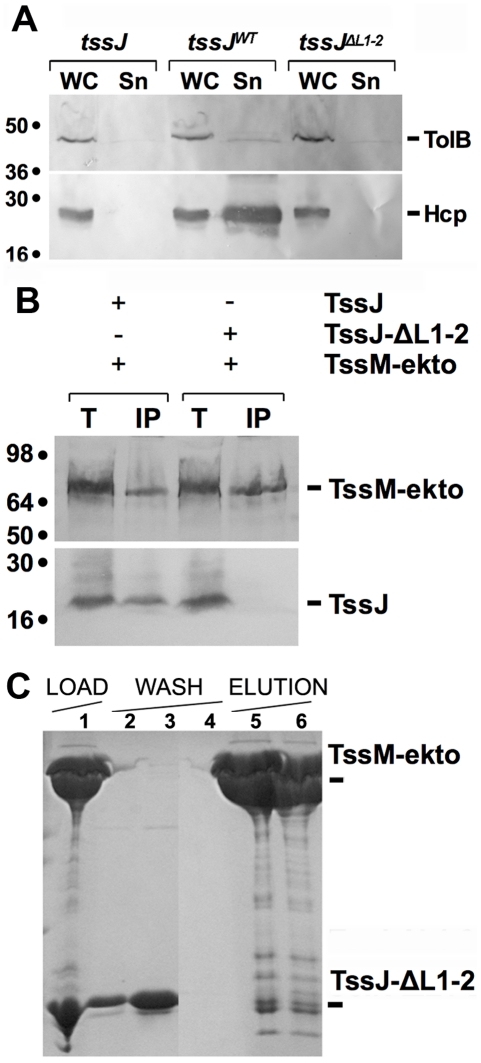
Figure 4. The L1-2 loop of TssJ is required for TssJ-TssM complex formation.
(A) In vivo Hcp release assay. HcpFLAG release was assessed by separating whole cells (WC) and supernatant (Sn) fractions from tssJ cells carrying the empty vector (tssJ), the vector encoding wild-type TssJ (tssJWT) or the vector encoding the TssJ-ΔL1-2 mutant (tssJΔL1-2). 2 ×108 cells and the TCA-precipitated material of the supernatant from 5×108 cells were loaded on a 12.5%-acrylamide SDS-PAGE and immunodetected using the anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (lower panel) and the anti-TolB polyclonal antibodies (lysis control; upper panel). (B) Solubilized extracts of E. coli K12 W3110 strain producing (+) or not (-) FLAG-tagged TssM-ekto and HA-tagged TssJ or TssJ-ΔL1-2 mutant were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG-coupled beads. The total solubilized material (T) and the immunoprecipitated material (IP) were loaded on a 12.5%-acrylamide SDS PAGE, and immunodetected with anti-HA (TssJ and TssJ-ΔL1-2; lower panel) and anti-FLAG (TssM-ekto; upper panel) monoclonal antibodies. Immunodetected proteins are indicated on the right. Molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. (C) Affinity purification of TssJ-ΔL1-2 with TRX-His6-TssM-ekto. The Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE shows the fractions of the purification steps (Load, fraction 1; Wash, fractions 2-4; Elution, fractions 5 and 6). The positions of the proteins of interest are indicated on the right.