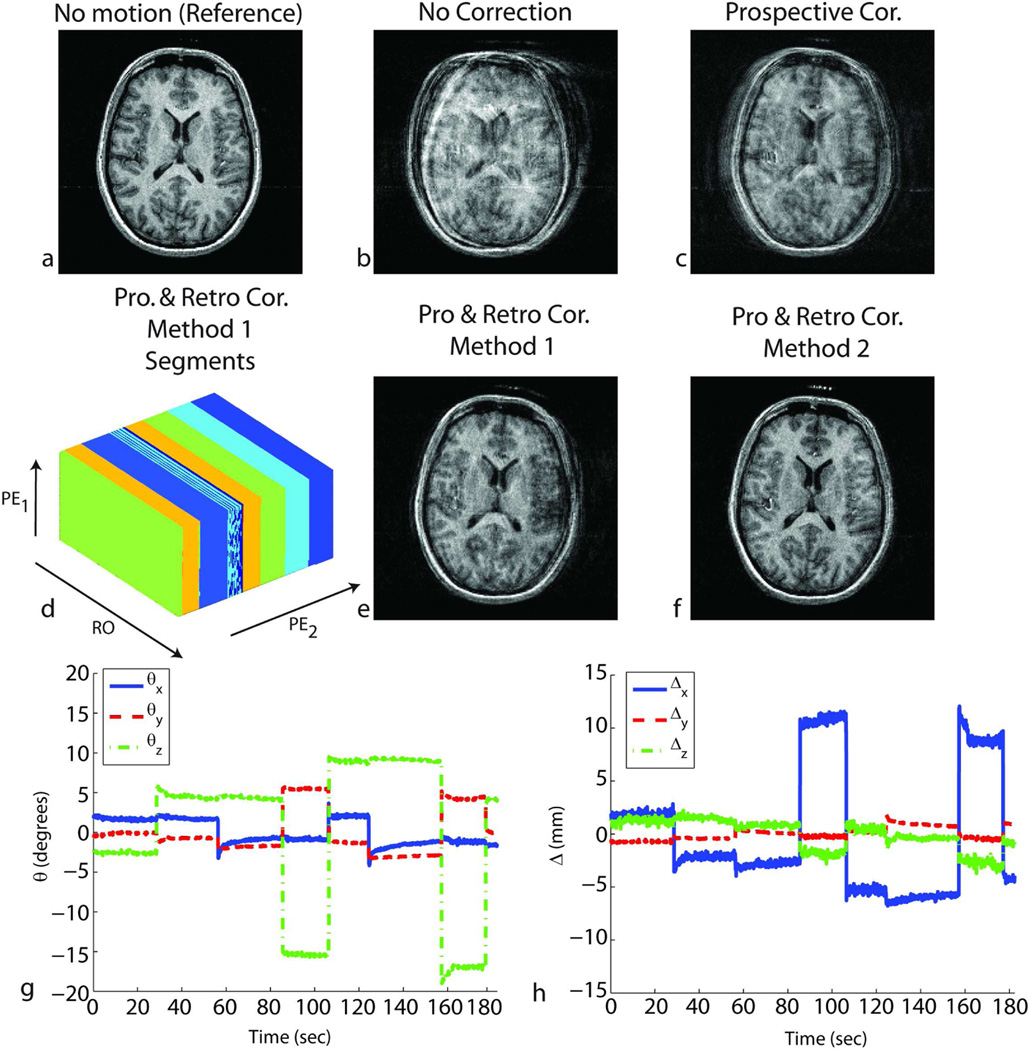
Figure 6.
Results of in-vivo experiments in the presence of shaking and nodding motion throughout the scan for subject 2. Without correction, the reconstructed image shows motion-related blurring (b). After prospective correction, residual artifacts remain due to the inaccurate cross-calibration between camera and scanner reference frames (c). Retrospective correction using method 2 – cross-calibration matrix-based autofocusing (f) improved the image quality. However, due to the large number of unknowns caused by the complicated motion pattern, method 1-segmentation based autofocusing did not yield good image quality (e). For method 1, the k-space segments in which the head position was approximately the same are shown in (d). RO corresponds to the readout axis, and PE1 and PE2 correspond to fast and slow phase encoding axes, respectively. Some of the estimated locations can fall onto the border separating two segments, which explains the color pattern observed on segment 3. The rotations (g) and translations (h) performed by the volunteer are also shown.