Figure 1.
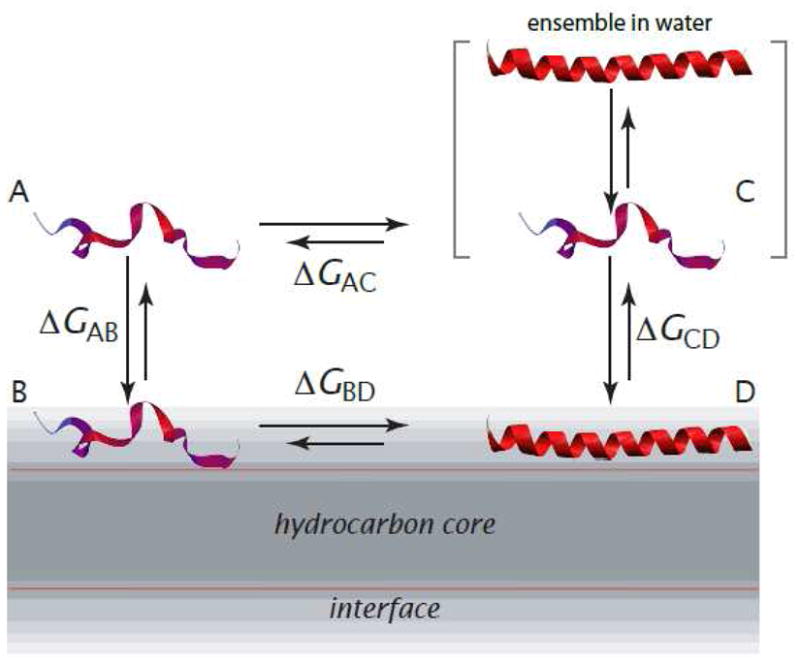
Thermodynamic cycle for partitioning-folding of an α-helical peptide in the membrane interface (modified from [7]). State A is the fully unfolded peptide in water; B is the fully unfolded peptide in the interface; C is the actual state of peptide in water, which is an ensemble of folded and unfolded conformations; and state D is the peptide in a α-helical conformation partitioned into the membrane interface. The conformation is not necessarily, and usually isn’t, fully α-helical. States A and B are virtual states that cannot be observed experimentally due to their low occupancy. The free-energy difference, ΔGAB, is computed using the experiment-based algorithm of Hristova and White [10]. The other free-energy differences are determined experimentally (Figure 2).
