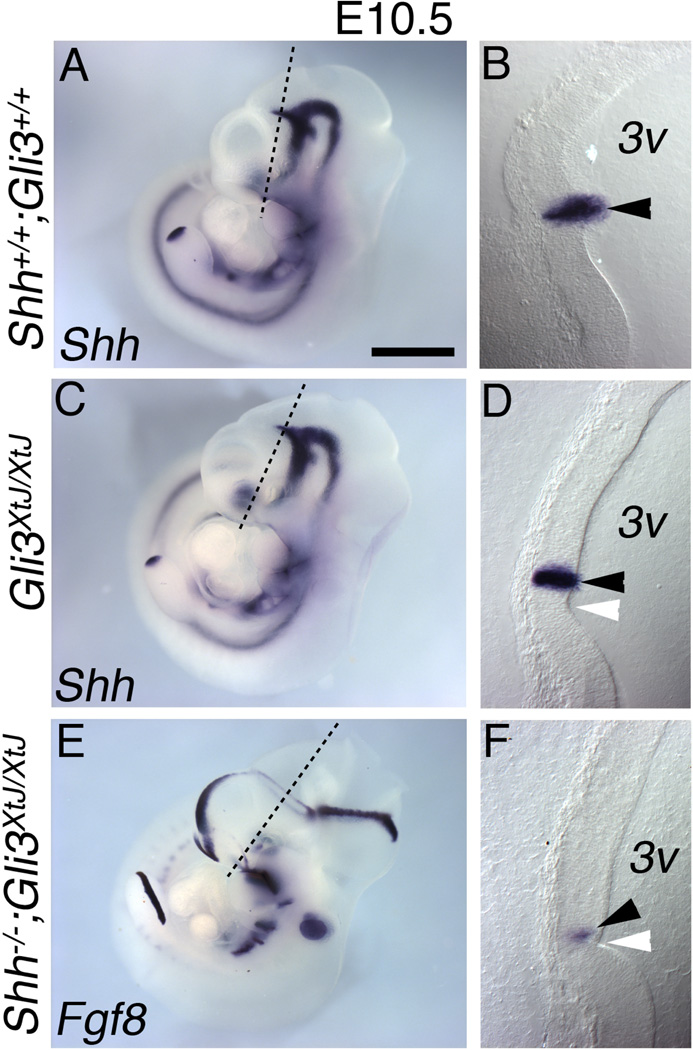
Figure 7. Identification of the ZLI as the site of the ectopic isthmus-like signaling source.
E10.5 wild type (A–B), Gli3XtJ/XtJ (C–D) and Shh;Gli3 double null (E–F) embryos processed for in situ hybridization for Shh (A–D) or Fgf8 (E–F). The embryos shown in A, C, and E were sectioned perpendicular to the ZLI at the position shown (black line) at 40µm, and sections are shown on the right (B,D,F). Note that panel E is the same as Figure 6E. In control embryos Shh expression appears near a morphological inflection in the interior wall of the third ventricle (3v) (B; arrowhead). In Gli3XtJ/XtJ and Shh;Gli3 double null embryos, this morphological feature remains (D,F; white arrowheads). In Gli3XtJ/XtJ embryos, Shh expression marks the ZLI (D; black arrowhead) as in wild type, but in Shh;Gli3 double nulls, a diencephalic Fgf8-expressing ring takes its place (F; black arrowhead). Scale bar is 1.2mm in A,C,E; 200µm in B,D,G.