Figure 3.
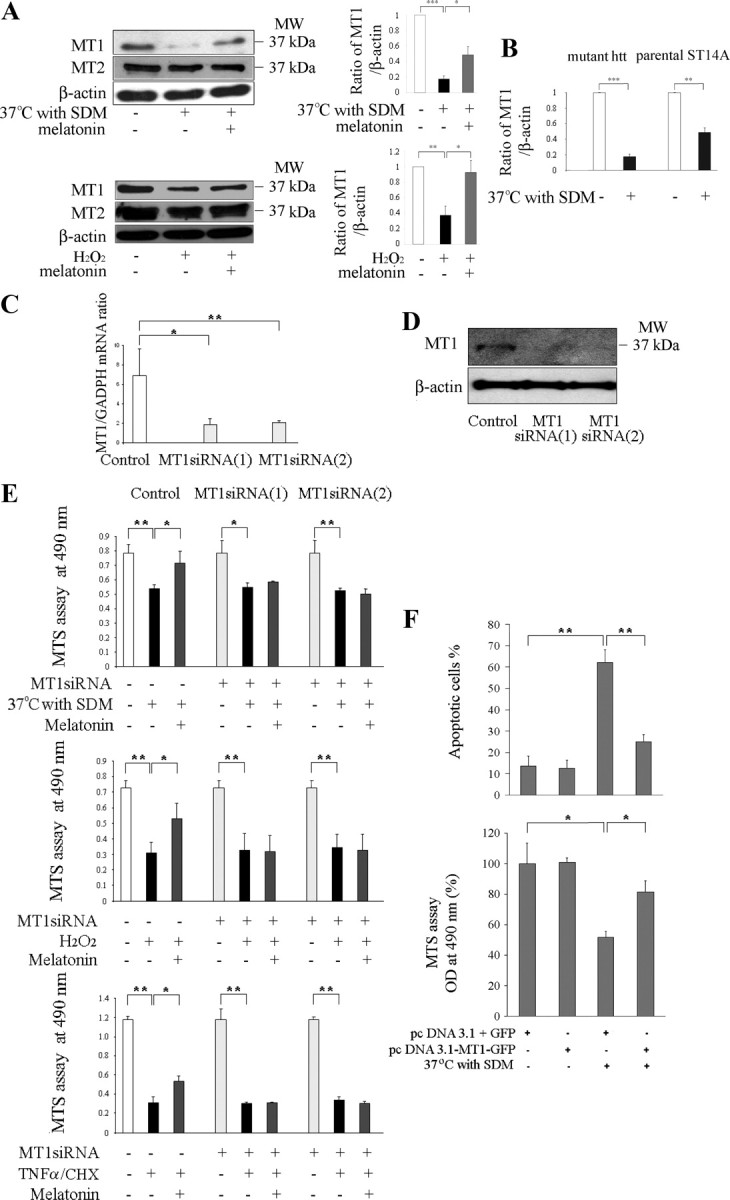
Knockdown of MT1 sensitizes cultured neurons to cell death; overexpression rescues them. Protein levels of MT1 and MT2 receptors were determined in mutant htt ST14A cells. During challenge by temperature shift in SDM or incubation for 18 h with 1 mm H2O2 (A), there is significant loss of MT1 receptor. In contrast, levels of MT2 receptor do not change. Pretreatment for 2 h with 5 μm melatonin significantly preserves levels of MT1 receptor (n = 3–4, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). B, The comparison of protein levels of MT1 receptors were determined in mutant htt ST14A cells and parental ST14A cells during challenge by temperature shift in SDM (n = 4, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). C–E, Neuroprotection by melatonin is eliminated by siRNAs, which target the MT1 receptor. Mutant htt ST14A cells were transiently transfected with MT1 siRNA 1 and siRNA 2 48 h before being challenged by the proapoptotic stimulus. Consequent depletion of MT1 mRNA was confirmed by qRT-PCR (C) and that of MT1 protein by immunoblotting (D). The mRNA for GAPDH and the protein for β-actin served as a loading controls for the PCR and the immunoblot, respectively (*p < 0.01, **p < 0.001). E, Neuroprotection afforded by melatonin is eliminated by knocking down levels of MT1 receptor. This phenomenon, apparent from MTS assays for cell viability, was observed in three different in vitro systems (i.e., mutant htt ST14A cells challenged by temperature shift in SDM, exposure to H2O2, or treatment with TNFα/CHX). F, Mutant htt ST14A cells challenged by temperature shift in SDM are rescued by an MT1 protein–GFP fusion but not by GFP alone. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1–MT1–GFP or pcDNA3.1/GFP, test and control plasmids, respectively. Forty-eight hours later, they were shifted to nonpermissive conditions for 18 h and then viewed under the fluorescence microscope. In the test group, stress caused significant cell death. In contrast, those cells expressing the MT1–GFP fusion protein were much more resistant to cell death. Parallel MTS assays of cell viability corroborated these results. Data are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. In all graphs, statistical significance is indicated: *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001.
