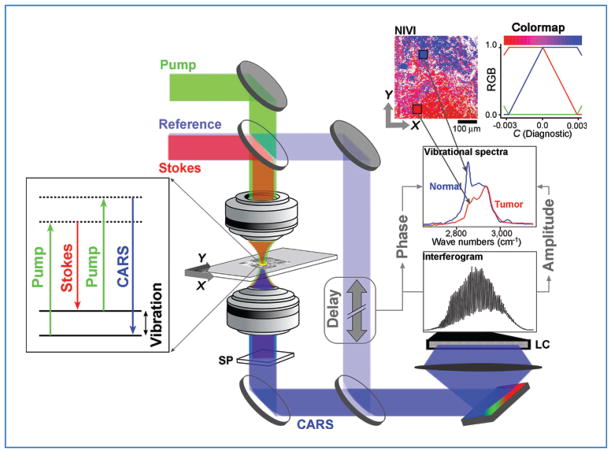
Figure 1.
SR-NIVI methodology. The pump and Stokes beams interact with the third-order polarizability of the tissue specimen to yield the CARS output, which is separated from the longer wavelength input pulses and fluorescence by a spectral filter (SP). A 0.3 numerical aperture 60× objective was used. A 1,200-grove/mm grating disperses the combined CARS/reference beam onto a 2,048-pixel line camera (LC). Extraction of vibrational spectra involves calculating the inverse Fourier transform (FT) of the interferogram, zeroing of the low frequency and negative components, and then calculating the FT to yield the spectra. SVD is used to transform the spectral pixels into a single diagnostic component C, which is color mapped by the red–blue range shown (blue = positive, C = normal; red = negative, C = tumor).