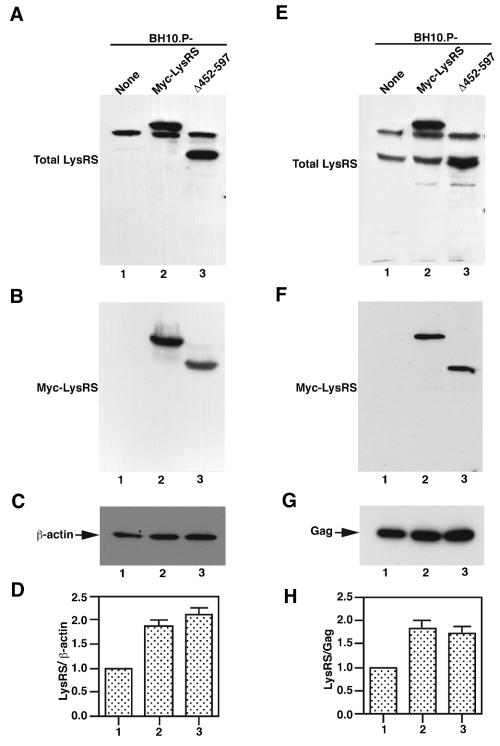
FIG. 2.
Effect of expression of Myc-LysRS and Δ452-597 LysRS upon the cytoplasmic and viral concentrations of LysRS. COS7 cells were cotransfected with BH10.P- and LysRS-encoding plasmids, viruses and cells were isolated and lysed, and the cell and viral lysates were analyzed by Western blotting, all as described in the legend of Fig. 1. (A through D) Cytoplasmic concentrations of LysRS. Western blot analysis of COS7 cell lysates, probed with either anti-LysRS (panel A), anti-Myc (panel B), or anti-β-actin (panel C). Panel D shows the LysRS/β-actin ratio as determined by quantitative analysis of the bands in panels A and C. The lanes in each panel represent COS7 cells transfected with the following plasmids: lane 1, BH10.P-; lane 2, BH10.P- and Myc-LysRS; and lane 3, BH10.P- and Δ452-597 LysRS. Myc-LysRS contains the Myc-containing sequence (MASMEQKLISEEDLNNG) appended to the N terminus of LysRS and was produced by cloning the PCR-amplified full-length LysRS cDNA into pcDNA1 (Invitrogen), into which sequences containing Myc had been inserted (7). Δ452-597 LysRS represents LysRS, whose C-terminal 146 amino acids were deleted and was also cloned into pcDNA1. (E through H) Western blots probing viral concentrations of LysRS. Viral lysates were probed with either anti-LysRS (panel E), anti-Myc (panel F), or anti-CA (panel G). Panel H shows the LysRS/Gag ratio determined from the data in panels E and G. Lanes in panels E through H represent viruses produced from cells transfected with: lane 1, BH10.P-; lane 2, BH10.P- and Myc-LysRS; and lane 3, BH10.P- and Δ452-597 LysRS. The bar graphs in panels D and H represent the means of experiments performed at least three times, and the error bars represent standard deviations.