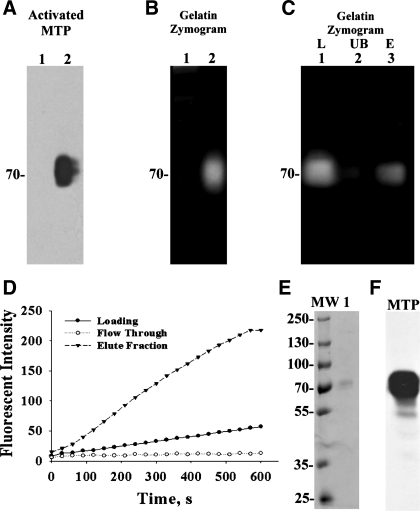
Fig. 5.
Production and purification of active MTP. RPMI-8226 multiple myeloma cells were exposed to basal media (A and B, lanes 1) or a pH 6.0 buffer (A and B, lanes 2) for 20 min. Proteins shed into extracellular millieu were collected, concentrated, and analyzed by immunoblotting for activated MTP using the mAb M69 (A, Activated MTP) or by gelatin zymography for the gelationolytic activity (B, Gelatin Zymogram) or for amidolytic activity using synthetic fluoresent substrate (D, loading). In C, the shed 70-kDa gelatinolytic activity (lane 1) was incubated with immobilized activated MTP mAb M69. The unbound fraction (lane 2) was collected. The mAb-captured proteins were eluted by glycine buffer pH 2.4 and immediately neutralized (lane 3). These three samples were analyzed by gelatin zymography. Active MTP shed by RPMI 8226 cells was purified by protease inhibitor affinity chromatography using p-aminobenzamidine. The amidolytic activity of active MTP was used to monitor the purification (D). The eluted proteins were further analyzed by SDS-PAGE for the purity of the preparation (E, lane 1) and by immunoblot for MTP (F). MW, molelcular weight markers.