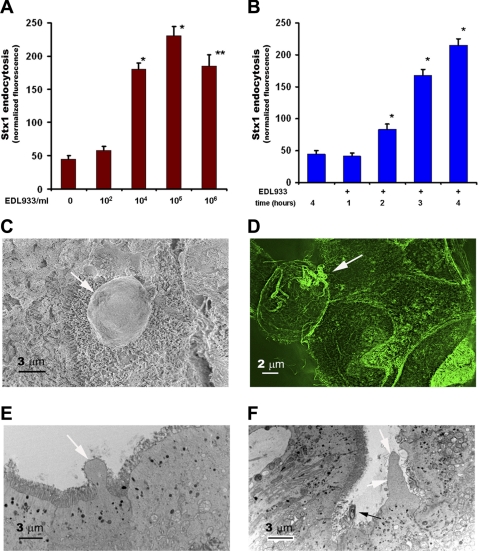
Fig. 1.
Infection of intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) significantly increases Shiga toxin 1 (Stx1) uptake by stimulation of macropinocytosis (MPC). A: uptake of Stx1-Alexa680 by T84 cells was stimulated by increasing concentrations of EDL933. B: 104 EDL933/ml significantly increased Stx1-Alexa680 uptake over time. n ≥ 6. The amount of endocytosed toxin in A and B was measured in total cell lysates in triplicates by fluorescent plate reader and normalized to the protein concentrations (n ≥ 6). *Significant compared with uninfected cells; **significant compared with 105 EDL933/ml. C: scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of T84 cells infected with EDL933 shows apical bleb (arrow) in places without attached bacteria. D: SIM image of EDL933-infected T84 cells and immunostained with phalloidin-AlexaFluor 488 demonstrates the F-actin nature of the apical bleb (arrow). Image represents the superimposition of 6 optical sections with 1-μm step. E and F: transmission EM (TEM) images of cecal epithelium from rabbits infected for 3 days with RDEC-H19A bacteria show that the apical blebs (white arrows in E and F) appear in places without and with attached bacteria (black arrow in F).