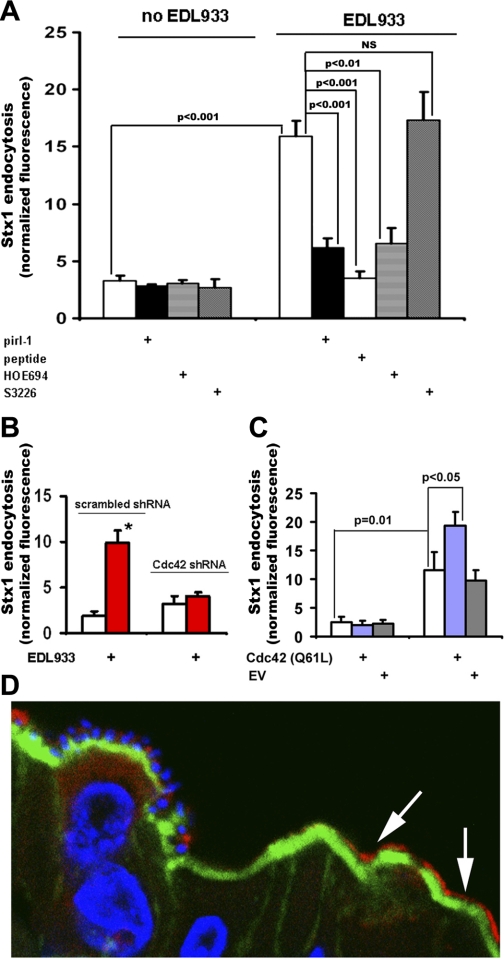
Fig. 4.
Cdc42 is necessary for EHEC-induced MPC in vitro and in vivo. A: pharmacological inhibition of Cdc42 activity decreases EHEC-stimulated Stx1 uptake in T84 cells; n ≥ 3. NS, nonsignificant. B: Cdc42 KD virtually abolishes the EHEC stimulation of Stx1 uptake. Cdc42KD data represent the combined data from 3 different short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs. *Significant compared with control (uninfected T84 cells transduced with lentivirus containing scrambled shRNA; P < 0.05; n = 8). C: constitutively active Cdc42 enhances the EHEC effect on Stx1 endocytosis but is not sufficient to stimulate MPC itself. EV, empty vector; n ≥ 3 for each condition. D: Cdc42 was active (red by anti-Cdc42-GTP Abs, with secondary AlexaFluor 568) in subset of rabbit cecal epithelial cells that often did not have attached bacteria; attached RDEC-H19A bacteria and T84 cell nuclei, blue by Hoechst (33); apical F-actin, green by phalloidin-AlexaFluor 488.