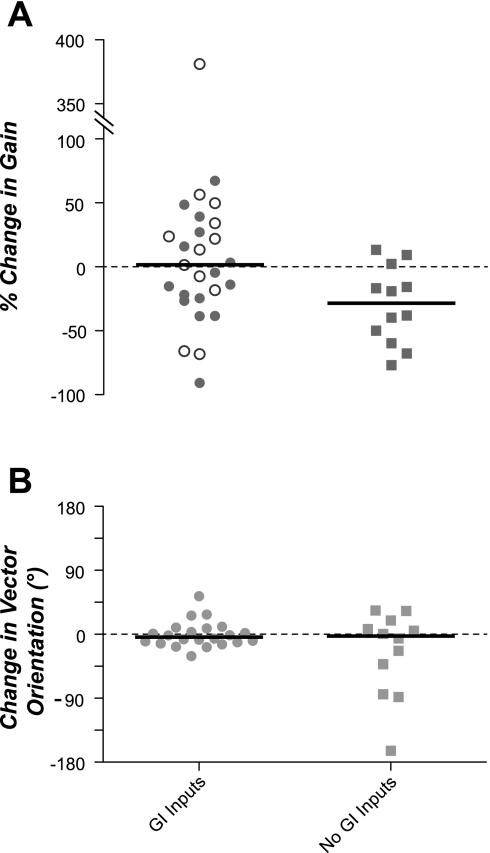
Fig. 7.
Effect of intragastric copper sulfate infusion on the gain of responses to wobble stimulation (A) and response vector orientation (B). In each panel, responses were segregated depending on whether a unit's spontaneous firing rate changed >30% after copper sulfate administration (GI inputs) or remained stable (no GI inputs). In A, ○ designate neurons with GI inputs whose firing rate increased after copper sulfate injection, whereas ● indicate neurons whose firing rate decreased. Horizontal lines designate median values.