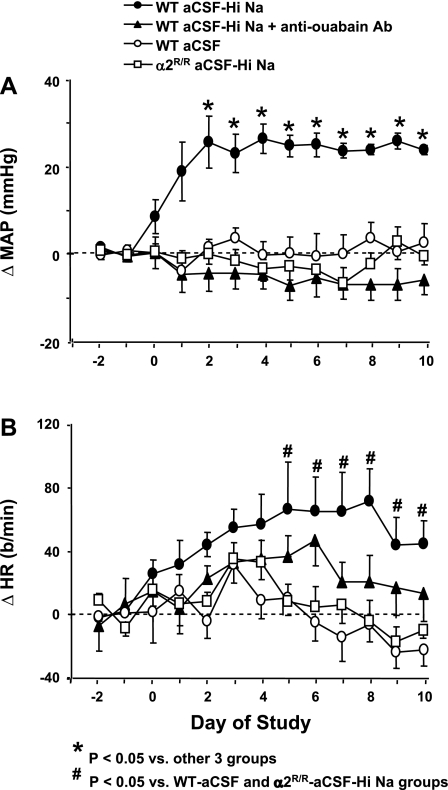
Fig. 1.
Twenty-four hour blood pressure and heart rate (HR) data obtained via telemetry before and after the start of intracerebroventricular (icv) infusions in wild-type (WT) mice or mice that are homozygous for 2-point mutations encoding a ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase α2-isoform (α2R/R). Infusions of various substances started on day 0 and continued until the end of the study on day 10. Values represent means ± SE of the changes from the baseline mean value in mean arterial pressure (ΔMAP; A) and ΔHR (B). Each value shown was in turn obtained from 24 MAP or HR measurements recorded hourly. aCSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid (rate of Na+ infusion, 0.6 nmol/min); aCSF-HiNaCl, NaCl-rich aCSF (rate of Na+ infusion, 5.0 nmol Na+/min); aCSF-HiNaCl + anti-ouabain Ab, aCSF-HiNaCl + an anti-ouabain antibody (0.65 nmol/day). Baseline MAP and HR (combined mean of day −1 and day −2 values) for α2R/R mice given aCSF-HiNa were 125 ± 5 and 546 ± 10; n = 10. The respective baseline mean MAP and HR for aCSF, aCSF-HiNaCl, and aCSF-HiNaCl + Ab treatment groups in WT mice were [in mmHg and beats/min (b/min), respectively] 115 ± 3 and 553 ± 20, n = 8; 117 ± 6 and 548 ± 20, n = 5; and 120 ± 4 and 592 ± 15, n = 9. *P < 0.05 vs. other 3 groups. #P < 0.05 vs. WT-aCSF and α2R/R-aCSF-HiNa groups.