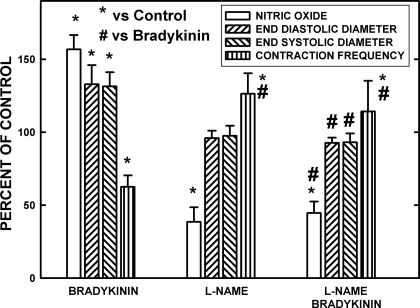
Fig. 5.
The effects of bradykinin at a maximal dosage (400 nA) and nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) suppression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) on [NO], end-diastolic diameter (EDD), end-systolic diameter (ESD), and frequency of contractions is shown for control and bradykinin-stimulated conditions. Seven vessels in 5 rats were used to obtain the data. Under control conditions, bradykinin raised the [NO] as the vessels dilated in diastole and systole, and the frequency of contraction declined. Very localized application of l-NAME decreased the resting [NO] to 38.5% of control, and the frequency of contraction increased. After l-NAME, bradykinin had no effects on the [NO], diameters, or frequency of contractions. Therefore, bradykinin predominately influenced rat mesenteric lymphatics through increasing NO production. *Significant change from control. #Significant change from bradykinin-induced responses.