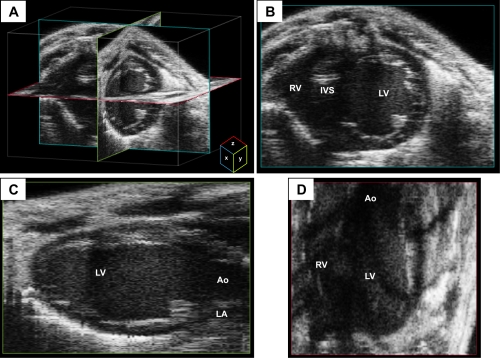
Fig. 4.
Three-dimensional (3-D) reconstruction imaging from a mouse heart. A: multiple two-dimensional (2-D) images obtained during a sweep of the transducer beam are used to create a dataset of voxels to reconstruct a 3-D image of the heart. Representative x-, y-, and z-planes of the heart are depicted in teal, green, and red, respectively. B–D: representative views from each of the planes are depicted. The x-plane image has good axial and lateral resolution of the 2-D image as a function of the transducer beam. The y- and z-planes have lower resolution than the x-plane because the resolution is a function of the size of the voxel in addition to that of the transducer beam. Images were acquired using the Vevo 2100 ultrasound system (Visualsonics). IVS, interventricular septum.