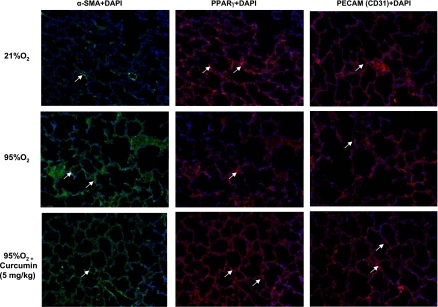
Fig. 8.
Molecular mechanism by which hyperoxia exposure inhibits alveolarization and how curcumin blocks this effect. Increase in α-SMA and decreases in PPARγ and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM, CD31) protein levels induced by 7 days of hyperoxia (95% O2) in vivo were corroborated by immunostaining. All these effects were blocked by concurrent treatment with 5 mg/kg curcumin. Representative images are shown, and locations of the specific proteins are indicated by white arrows; nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Images are representative of results from 3 experiments.