Figure 2.
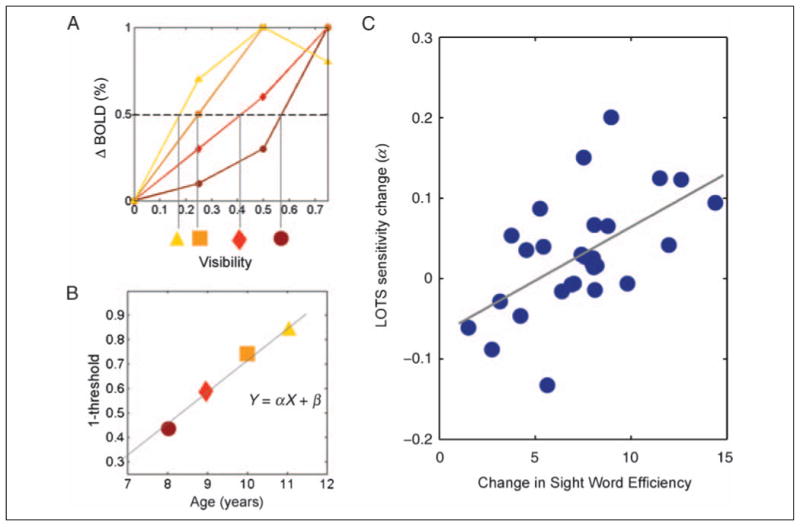
Longitudinal change in LOTS predicted by the change in SWE. (A) Threshold visibility is the visibility level that gives rise to half the maximum fMRI response, and sensitivity is (1 – threshold). In this example, the threshold decreases (sensitivity increases) across four measurements (brown to yellow shapes). (B) Change in sensitivity is computed as the slope (α) of a line fit to the sensitivity measures over time. Similarly, behavioral change is computed as the slope of a line through the raw behavioral scores over time. Subjects with fewer than three usable data sets are excluded from this analysis. (C) The correlation between longitudinal change in LOTS sensitivity and SWE is highly significant (r = 0.564, SE = ±0.11; SE is computed by bootstrapping, n = 28).
