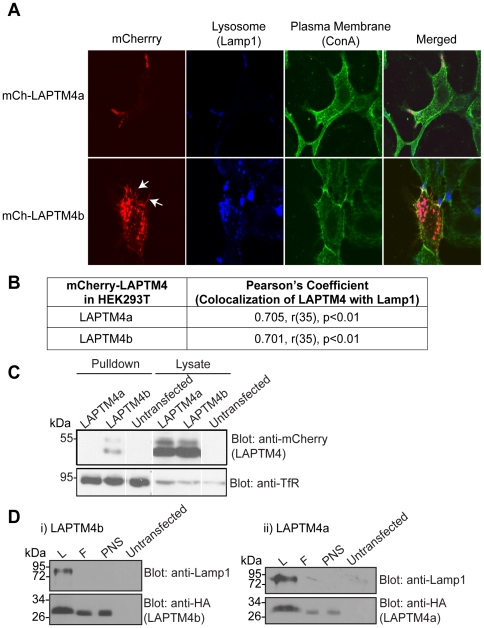
Figure 2. Both LAPTM4 proteins localize to lysosomes, but LAPTM4b is uniquely present also at the cell surface.
(A) 24 hrs post transfection the plasma membrane (ConA, green) of Hek293T cells expressing mCh-LAPTM4a (red, top) or mCh-LAPTM4b (red, bottom) was stained, cells were fixed and incubated with anti-Lamp1 antibodies (blue). White arrows indicate mCh-LAPTM4b in hair-like protrusions. Cells were imaged using LSM510 and subcellular localization was assessed using Volocity 5.4.1. (B) Colocalization of LAPTM4s with the lysosomal marker Lamp1 was expressed in terms of the Pearson's correlation coefficient. Degrees of freedom are noted as (r), level of significance as (p). n = 37 for LAPTM4a and LAPTM4b. (C) Untransfected or transfected (mCh-LAPTM4a-WT or mCh-LAPTM4b-WT) Hek293T cells were subjected to cell surface biotinylation, lysis, pulldown with streptavidin agarose beads and separation on SDS-PAGE. Cell surface biotinylation of the Transferrin receptor (TfR) was used as a positive control. (D) Biochemical evidence for the presence of LAPTM4 proteins in lysosomes: Lysosomal fraction from Hek293T cells overexpressing HA-LAPTM4a or b were isolated as described in the Materials and Methods section. Post nuclear supernatant (PNS) was loaded on a magnetic column, the flowthrough (F) was collected and upon removal of the column from the magnet the lysosomal fraction (L) was eluted. Western blotting shows significant enrichment of endogenous Lamp1 in the L fraction, as well as the presence of LAPTM4a or b.