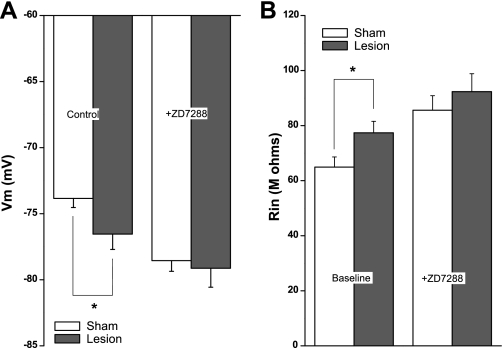
Fig. 1.
L5 pyramidal neurons from freeze-lesioned rats have depolarized membrane potentials (Vm) and increased input resistances (Rin). A: the resting Vm of pyramidal neurons near the freeze lesion is significantly hyperpolarized compared with sham-operated control animals. This difference is not significant after hyperpolarization-activated nonspecific cation (HCN) channel inhibition with ZD7288. B: the Rin of pyramidal neurons near the freeze lesion is significantly higher than that of sham-operated control animals. This difference is not significant after HCN channel inhibition. *P < 0.05.