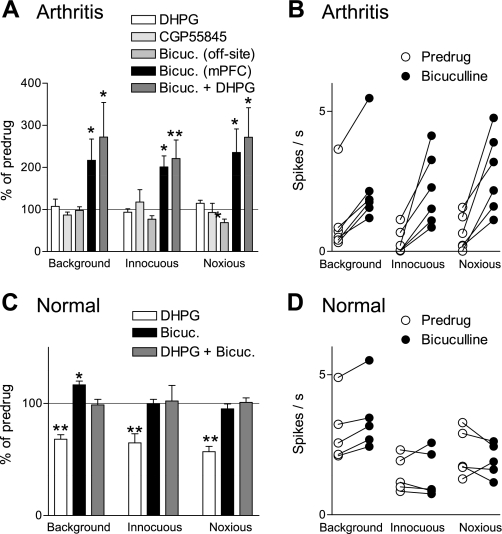
Fig. 4.
Pain-related GABAergic inhibition of mPFC neurons can be activated by mGluR1/5. Summary of the effects of GABA receptor antagonists and mGluR1/5 agonist on mPFC neurons in arthritis (5–6 h postinduction; A) and under normal conditions (B). A: administration of DHPG (mGluR1/5 agonist, 100 μM; n = 5) or 2S(-3-[[(1S)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]amino-2-hydroxypropyl]phenylmethyl)phosphinic acid hydrochloride (CGP55845; GABAB receptor antagonist, 500 μM) into the prelimbic mPFC had no effect (n = 5 neurons). Administration of bicuculline (Bicuc.; GABAA receptor antagonist, 1 mM) into the prelimbic mPFC (n = 6), but not ACC (n = 5), increased background and evoked activity. In the presence of bicuculline, DHPG (100 μM; n = 5) had no effect. B: raw data show the facilitatory effect of bicuculline (1 mM) in individual mPFC neurons in arthritis. Each symbol represents background or evoked activity (spikes/s) before and during drug administration. C: administration of DHPG (100 μM; n = 6) into the prelimbic mPFC inhibited background and evoked activity. Bicuculline alone (1 mM; n = 5) had little or no effect but blocked the inhibition by DHPG (n = 5). D: raw data show the effect of bicuculline (1 mM) in individual mPFC neurons under normal conditions. Each symbol represents background or evoked activity (spikes/s) before and during drug administration. A and C: bar histograms show spikes/s averaged across the sample of neurons (mean ± SE) normalized to predrug controls (set to 100%). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (compared with predrug values, ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests).