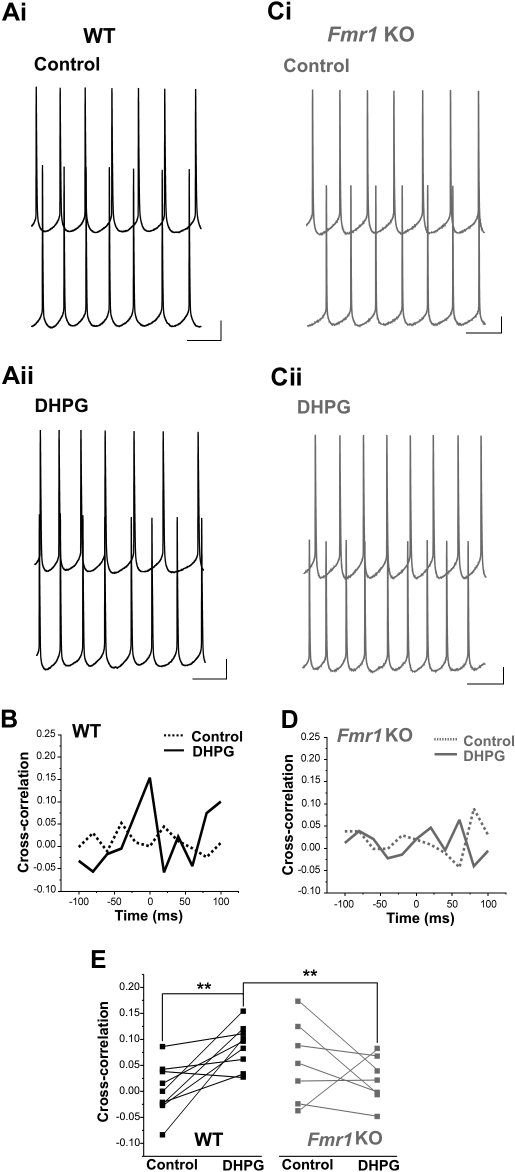
Fig. 5.
DHPG-induced AP synchronization is reduced in Fmr1 KO pyramidal neurons. A: simultaneous recordings of evoked AP firing in 2 WT pyramidal neurons. AP synchronization was low under control conditions (i) and then increased with DHPG application (ii), as illustrated by the increase in cross-correlogram central peak value (B; bin width = 20 ms). C: example of a pair of Fmr1 KO pyramidal neurons that similarly exhibited low AP synchronization under control conditions (i) but did not show an increase with DHPG application (ii). D: the cross-correlogram for the cell pair in C lacks a defined central peak under both conditions, indicating a lack of AP synchronization. E: DHPG induced a significant increase in the synchronization of evoked APs in WT but not Fmr1 KO mice. AP cross-correlation in DHPG was also significantly greater in WT than in Fmr1 KO mice (n = 9 WT pairs and 7 Fmr1 KO pairs). **P < 0.01. Calibrations: 10 mV, 200 ms.