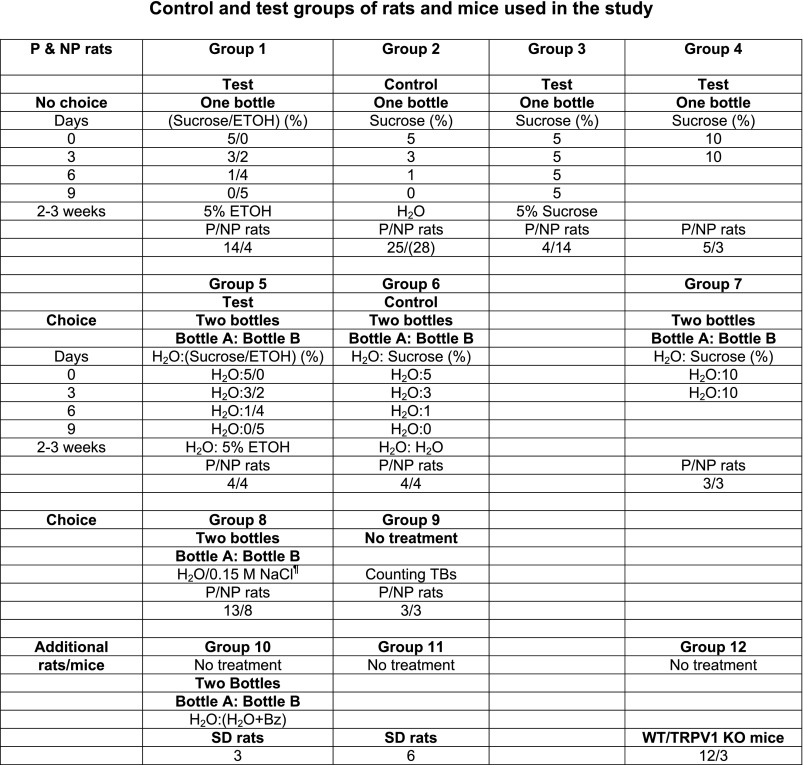
Fig. 1.
Control and test groups of rats and mice used in the study. Seventy-five alcohol-preferring (P) and 71 alcohol-nonpreferring (NP) rats were used in this study. Of these, 59 P and 60 NP rats were given 7 different treatments in a no-choice (groups 1–4) or choice (groups 5–7) paradigm. For the no-choice paradigm, group 1 is the test group and group 2 is the control group. For the choice paradigm, group 5 is the test group and group 6 is the control group. P and NP rats in each of groups 1–3, 5, and 6 were either used for chorda tympani (CT) nerve recordings or killed, with their tissues harvested for gene expression and protein analysis. P and NP rats in groups 4 and 7 were used for behavioral studies or for collection of tissues for gene expression studies. ¶In group 8, P and NP rats were used for 2-bottle preference tests for NaCl, NaCl+ benzamil (Bz), and NaCl+Bz+ Maillard reacted peptides conjugated with galacturonic acid (GalA-MRPs). When Bz was used with the salt solution, Bz was also added to the second bottle containing H2O. The fluid intakes were monitored when bottle A and bottle B contained the following solutions (bottle A/bottle B): 1) H2O/0.15 M NaCl; 2) (H2O+5×10−6 M Bz)/(0.15 M NaCl+5×10−6 M Bz); and 3) (H2O+5×10−6 M Bz+0.25% GalA-MRPs)/(0.15 M NaCl+5×10−6 M Bz+0.25% GalA-MRPs). In group 9, lingual epithelium was isolated by collagenase treatment from P and NP rats and used for counting the number of taste buds (TBs). In addition to P and NP rats, we used Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (groups 10 and 11). Three rats were used to test the effect of Bz on H2O intake. An additional 6 rats were used to test the effect of U73122 and BAPTA on sweet responses. We also used 3 wild-type (WT; group 12) and 3 TRPV1 knockout (KO; group 12) mice to test the effect of TRPV1t agonists on the CT response to 0.15 M NaCl+5×10−6 M Bz. An additional 5 WT mice (group 12) were used to construct a cDNA library from fungiform (FF) TBs, circumvallate (CV) TBs and nongustatory lingual epithelium devoid of TBs (NG Epi) to screen for TRPM5, α-gustducin, and TRPV1.