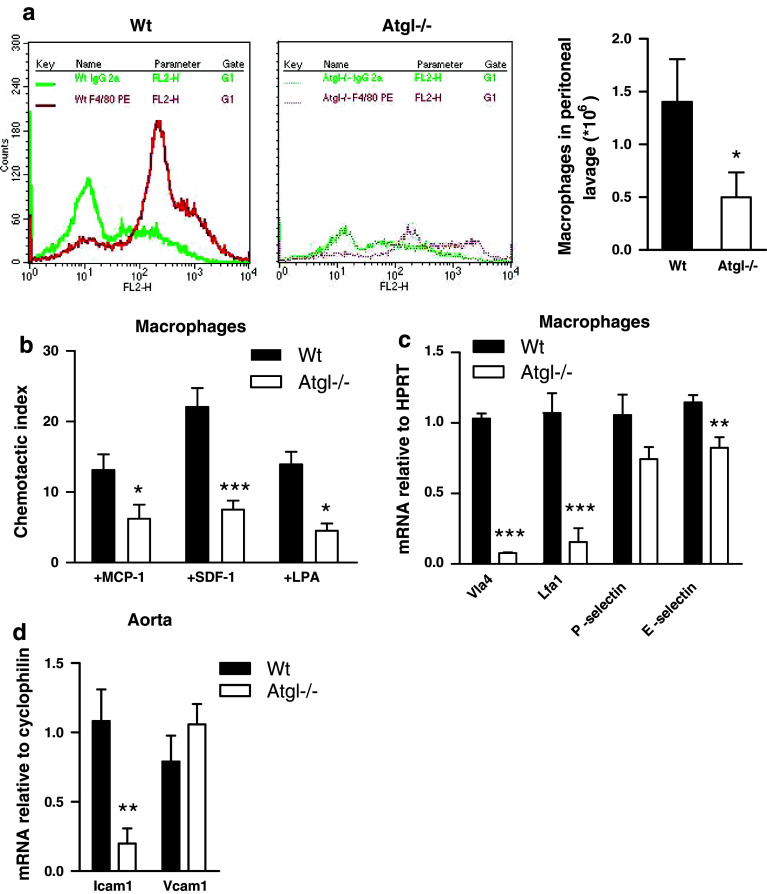
Fig. 2.
Reduced migration of Atgl−/− macrophages (a) Wt and Atgl−/− mice were challenged with 3% thioglycolate by intraperitoneal injection. Peritoneal lavage was collected 3 days after injection, and the macrophage-specific marker F4/80 was measured by flow cytometry. Data represent means (n = 6) of three independent experiments. (b) Macrophages from Wt and Atgl−/− mice were added to the upper chamber of transwell plates and were allowed to migrate through the membrane (pore size: 5 μm) into the lower chamber containing DMEM in the absence and presence of MCP-1 (50 ng/ml), SDF-1 (60 ng/ml) or LPA (9 ng/ml) at 37°C for 4 h. Migrated cells were counted by flow cytometry. Chemotactic indexes were calculated from the ratio of the cells that had migrated in the presence or absence of the respective chemoattractant. Data of two independent experiments are presented as means (n ≥ 5) ± SEM. c, d Total RNA was isolated from Wt and Atgl−/− (c) macrophages and (d) aorta, reverse transcribed, and mRNA expression of (c) very late antigen 4 (Vla4), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (Lfa1), P-selectin, E-selectin and (d) vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (Vcam1) and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (Icam1) was determined by real-time PCR including normalization to (c) HPRT and (d) cyclophilin A. Data are expressed as mean values (n = 6) of two independent experiments ±SEM performed in triplicate repeats. *p < 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001