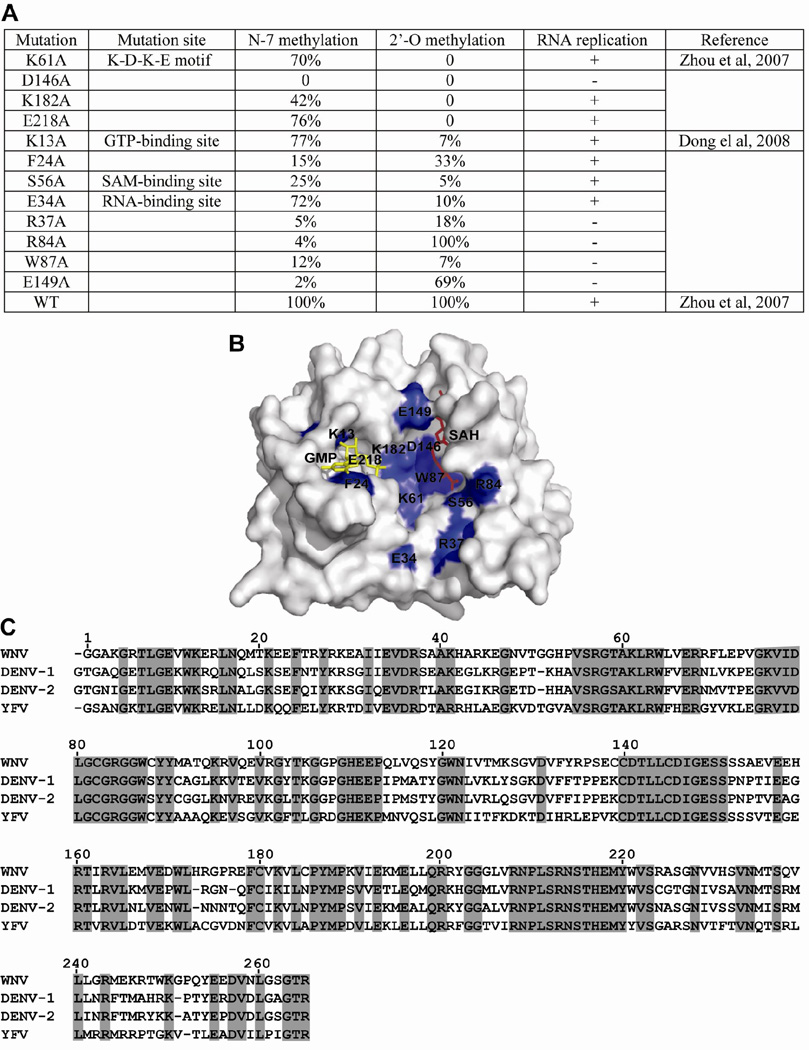
FIG. 5. Correlation between N-7 methylation and WNV replication.
(A) Effects of a panel of mutations of WNV MTase on cap methylations and viral replication. Mutations of representative amino acids within the K-D-K-E motif, GTP-binding site, SAM-binding site, and RNA-binding site were assayed for their effects on cap methylation and viral replication. N-7 methylation was determined by conversion of GpppA-RNA→m7GpppA-RNA. 2'-O methylation was determined by conversion of m7GpppA-RNA→m7GpppAm-RNA. WT methylation activity was set as 100%. Viral RNA replication was indicated by plaque formation upon transfection of genome-length RNA containing the indicated mutation. Symbols “+” and “−“ indicate that genome-length RNA containing the MTase mutations are replicative or non-replicative, respectively. Note that the K-D-K-E motif forms the active site for 2'-O methylation; the D146 residue of the K-D-K-E motif is essential for N-7 methylation (Ray et al., 2006). (B) Crystal structure of WNV MTases displaying the mutated amino acids. Mutated residues (blue) from (A) are shown on the surface presentation of the WNV MTase [PDB code 2OY0 (Zhou et al., 2007)]. GTP and SAH molecules are colored in yellow and red, respectively. (C) Sequence alignment of flavivirus MTases. The MTase sequences of WNV, DENV-1, DENV-2, and YFV are derived from GenBank accession number AF404756, DVU88535, U87411, and YFU17-66, respectively. The alignment was performed using GCG software (Genetics Computer Group). Identical amino acids among all MTases are shaded.