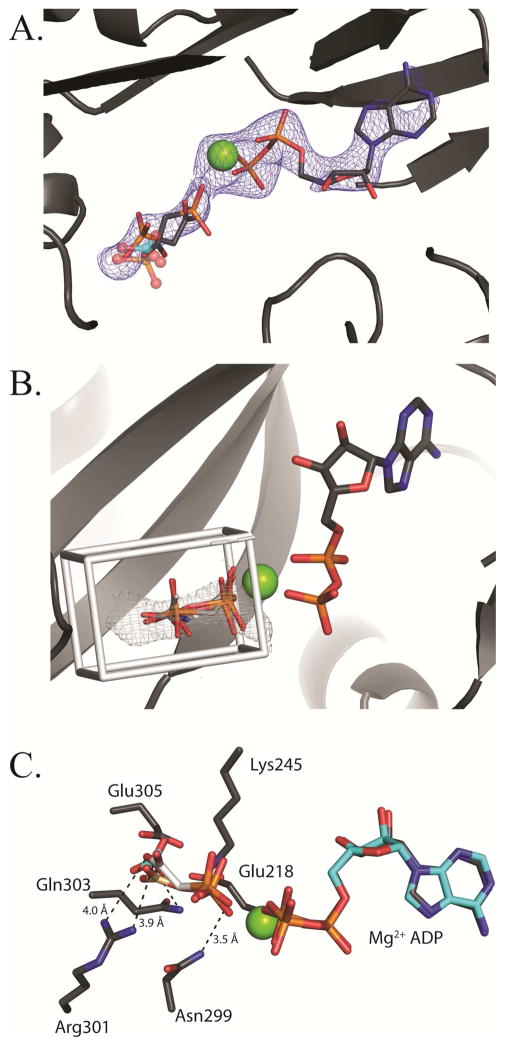
Figure 5. Binding of phosphonoacetate in the BC domain active site.
(A) Phosphonoacetate is modeled in two conformations into a lobe of electron density observed in the BC domain active site on the top face (chain C) of tetramer 2. The Fo-Fc omit electron density contoured at 2.5 σ is shown in blue. A structural superposition of E. coli BC with bound bicarbonate (semi-transparent, cyan-colored ball and stick representation; pdb id = 3G8C) and phosphate (semi-transparent, CPK-colored ball and stick representation; pdb id = 1DV1) reveals that both phosphate and bicarbonate share the same binding site. The positions of both the carboxyl and phosphonate moieties of phosphonoacetate align well with the shared binding site for phosphate and bicarbonate. (B) AutoDock 4.2 modeling of carboxyphosphate, phosphonoacetate, acetyl phosphate and carbamoyl phosphate in the active site of BC. The docking grid box was extended to fully encompass the electron density for phosphonoacetate. All calculated docking poses line up closely with the observed Fo-Fc omit electron density. (C) An overlay of docked carboxyphosphate (brown carbon CPK coloring) with one conformation of phosphonoacetate (white carbon CPK coloring). Residues within interacting distance of phosphonoacetate are shown.