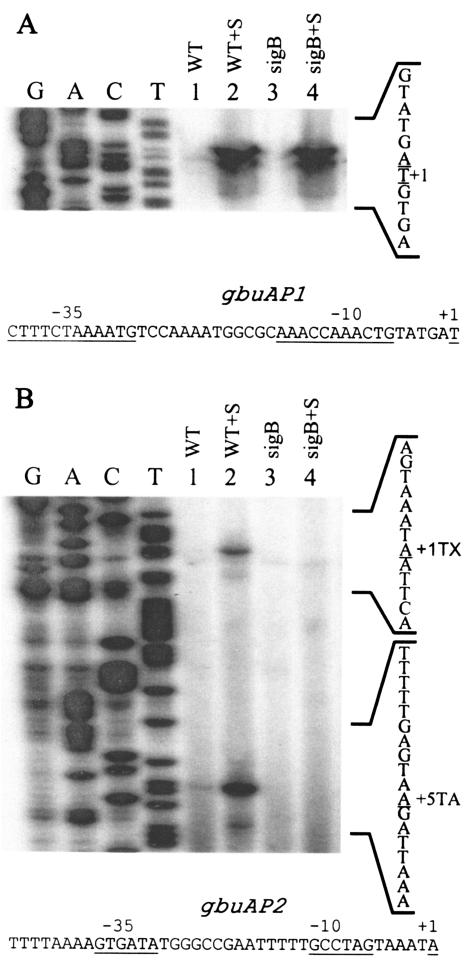
FIG. 2.
Primer extension analyses of transcripts originating from the gbuA promoter. Cells were grown in BHI (OD600, ∼0.5), harvested, washed, and resuspended in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer with 50 mM glucose (final concentration). NaCl was added to a 3% final concentration to one portion of the cells. After a 20-min incubation, RNA was extracted, and 50 μg of each RNA sample was used as a template for extension of the labeled AEX3 primer. (A) Transcripts originating from the gbuAP1 promoter; (B) transcripts originating from the σB-dependent gbuAP2 promoter. Both panels were derived from the same autoradiogram. Lane 1,10403S (WT); lane 2, 10403S plus 3% NaCl (WT+S); lane 3, LMA2B (sigB::Kan) (sigB); lane 4, LMA2B(sigB::Kan) plus 3% NaCl (sigB+S). The sequence ladder was derived from sequencing reactions using the AEX3 primer, and the reverse complement sequence is shown to the right. The nucleotides corresponding to the 3′ end of the primer extension products (transcription initiation site) are underlined. The extension products in panel B are labeled +1TX (σB-dependent transcription initiation site) and +5TA (extension product mapping to +5 relative to translation). The top strand sequences of the regions 5′ to the gbuAP1 and gbuAP2 transcription start sites are shown below each panel with the relevant +1, −10, and −35 regions indicated.