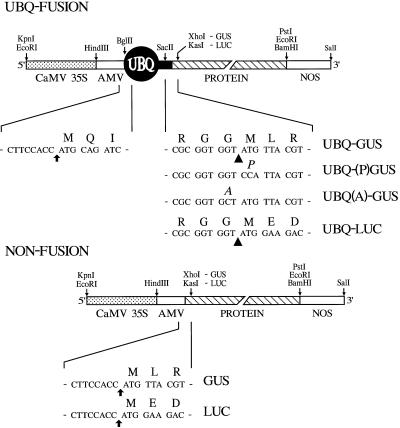
Figure 2.
Structures of the various gene constructions used for expressing GUS and LUC as UBQ fusions. The UBQ fusion vector was designed to contain the CaMV 35S promoter, the AMV 5′-UTR, and the sequence encoding UBQ. Appended to the UBQ sequence is DNA encoding GUS or LUC, followed by the polyadenylation signals from NOS. The nucleotide sequences surrounding the translational initiation site (arrows) and the UBQ/protein junction are shown. Convenient restriction sites used for assembly are indicated; the restriction sites within the 5′-coding region of GUS and LUC are XhoI and KasI, respectively. The structure and sequences of the respective nonfused genes that were used as controls are also shown. Arrowheads indicate the predicted cleavage site by Ubps. UBQ-(P)GUS contains GUS with its N-terminal Met changed to Pro; UBQ(A)-GUS contains UBQ with its C-terminal Gly changed to Ala.