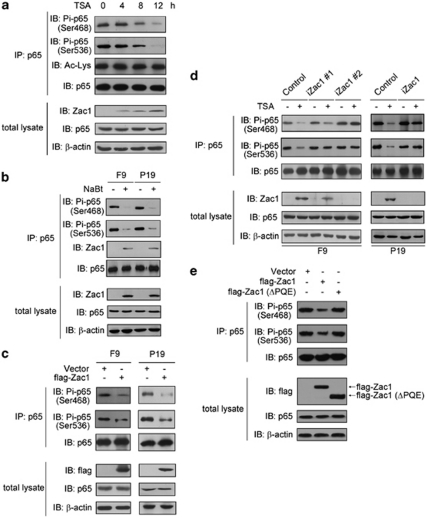
Figure 6.
Zac1 inhibits NF-κB p65 subunit phosphorylation at Ser468 and 536 residues. (a) F9 cells were exposed to 20 ng/ml TSA for the indicated time periods and then p65 protein was immunoprecipitated using an anti-p65 antibody. Total p65 and p65 phosphorylation at Ser468 and Ser536 were visualized using corresponding antibodies. Acetylation of p65 was detected using an antibody specific to acetylated lysine. Zac1 and p65 protein levels in the total lysate were also shown. (b) F9 and P19 cells were treated with 1.5 mM NaBt for 12 h, and then p65 phosphorylation levels at Ser468 and Ser536 were detected as described in panel a. The Zac1 proteins interacting with p65 are also shown. (c) F9 and P19 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding flag-Zac1. Forty-eight hours after transfection, p65 phosphorylation levels at Ser468 and Ser536 were detected. The level of transfected Zac1 (detected by anti-flag tag antibody) and the total p65 level (detected by anti-p65 antibody) in the total lysate were also shown. (d) F9 and P19 cell clones were treated with 20 ng/ml TSA (12 h). Cellular Zac1, p65, Ser468-, and Ser536-phosphorylated p65 were examined as described above. (e) F9 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Forty-eight hours later, p65 phosphorylation levels at Ser468 and Ser536 were detected. The level of transfected Zac1 and total p65 level in cell lysate were also shown