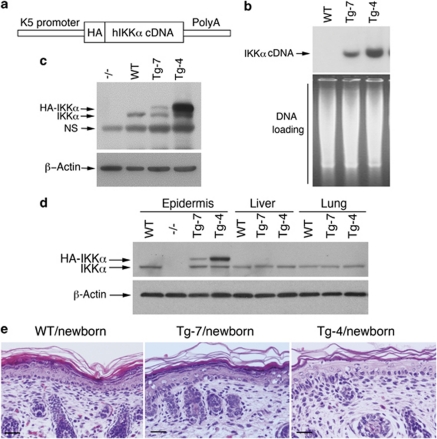
Figure 1.
Normal skin development in mice overexpressing different levels of the IKKα transgene. (a) Construct of IKKα transgenic mice. HA, hemagglutinin; hIKKα, human IKKα; K5, keratin5. (b) Southern blotting was used to determine IKKα transgene in IKKα transgenic mice. An N-terminal IKKα cDNA was used as a probe for Southern blotting. BamHI was used to digest genomic DNA, stained with ethidium bromide, isolated from the skin specimens of mice. Agarose gel image was used as the DNA loading control. (c) Western blotting was used to determine transgenic IKKα levels in the skin specimens of mice. HA-IKKα, HA-tagged transgenic IKKα; NS, nonspecific band; WT, wild-type mice; −/−, Ikkα−/− mice. (d) IKKα levels in the epidermis, liver, and lungs of Tg-4, Tg-7, WT, and Ikkα−/− (−/−) mice, as detected by western blotting. HA-IKKα, HA-tagged transgenic IKKα; −/−, Ikkα−/− mice; β-actin, a loading control. (e) Histology of hematoxylin and eosin-stained skin sections of WT, Tg-7, and Tg-4 newborn mice. Scale bars=150 μm