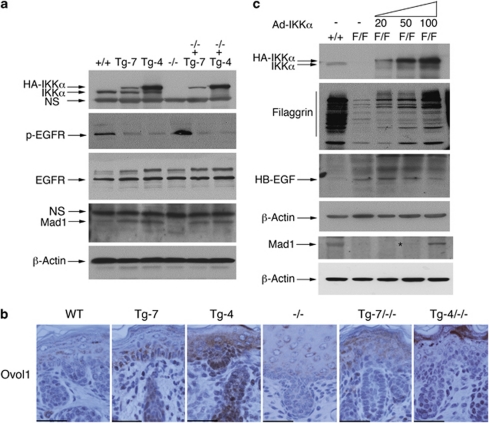
Figure 6.
Effects of IKKα doses on EGFR activity, HB-EGF, Mad1 and Ovol1 levels, and terminal differentiation in the skin. (a) Protein levels from the epidermis of WT (+/+), Tg-7, Tg-4, Ikkα−/− (−/−), Tg-7/Ikkα−/− (−/−+Tg-7), and Tg-4/Ikkα−/− (−/−+Tg-4) newborn mice were detected using western blotting. β-Actin was used as protein loading control. (b) Ovol1 expression levels in the paraffin-embedded skin sections of indicated newborn mice were detected with immunohistochemical staining. Dark brown color indicates positive staining; blue color indicates hematoxylin counterstaining. Scale bars=150 μm. (c) Primary cultured keratinocytes were infected with different amounts of adenoviruses expressing IKKα. After 5 days of viral infection, protein levels of HB-EGF, filaggrin, and Mad1 were determined using western blotting. +/+, keratinocytes isolated from WT mice; F/F, keratinocytes isolated from IkkαF/F/K5.Cre mice 15; 20, 50, and 100 μl of cell culture supernatant containing the adenovirus expressing IKKα (Ad-IKKα) was added into cultured keratinocytes. The angle sign at the top of the panel indicates increased Ad-IKKα doses