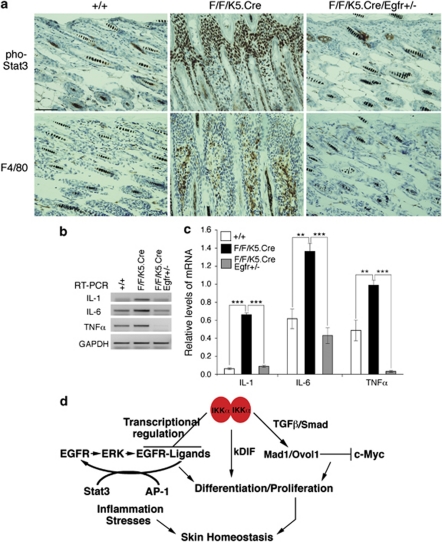
Figure 8.
IKKα deletions cause skin inflammation in mice. (a) Stat3 activity and macrophages (F4/80) in the skin sections of WT (+/+), IkkαF/F/K5.Cre (F/F/K5.Cre), and IkkαF/F/K5.Cre/Egfr+/− (F/F/K5.Cre/Egfr+/−) mice were detected by immunohistochemical staining. pho-, phosphorylated; brown color indicates positive stained cells; blue color indicates hematoxylin counterstaining. Scale bars=200 μm. (b) Relative levels of TNFα, IL-6, and IL-1 with mRNA WT (+/+), IkkαF/F/K5.Cre (F/F/K5.Cre), and IkkαF/F/K5.Cre/Egfr+/− (F/F/K5.Cre/Egfr+/−) skin samples detected using reverse transcriptase-PCR detected by gel. Levels of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA were used to normalize the expression levels of these cytokines. (c) The statistic results for (b). **P<0.01 (t-test); ***P<0.001 (t-test). Each point (n=3) used. (d) A working model of how IKKα maintains skin homeostasis. Transforming growth factor-β and transcription regulation were previously described.15, 20 kIDF, keratinocyte-inducible differentiation factor(s).28 Transcriptional regulation was previously described.15 Arrow indicates upregulation. Line with vertical line at the end indicates downregulation