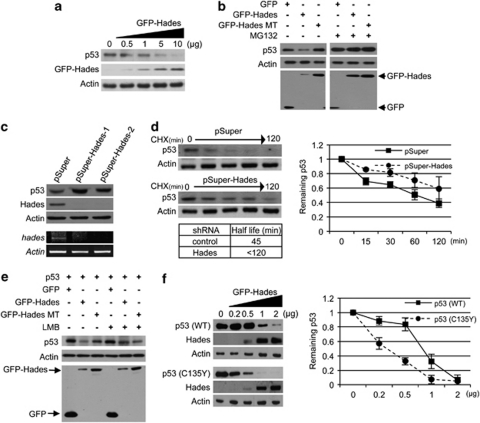
Figure 2.
Hades reduces the cytoplasmic p53 level. (a) Immunoblot analysis showed that ectopically expressed Hades reduces the level of endogenous p53. U2OS cells were transfected with increasing amounts of GFP-Hades plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, the level of p53 protein was examined by immunoblot analysis. (b) Hades decreases the level of ectopically expressed p53, depending upon its ubiquitin ligase activity. H1299 cells were cotransfected with 1 μg of each indicated plasmid for 24 h and treated with 10 μM MG132 for 4 h. (c) Generation of stable Hades-knockdown MCF7 cells using the shRNA, pSuper-Hades. After selection for 14 days in media containing G418 (500 μg/ml), hades mRNA levels were measured by RT-PCR and the levels of endogenous Hades and p53 proteins were measured by immunoblotting. (d) Ablation of Hades increases p53 stability. Stable Hades-knockdown MCF7 cells were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX, 150 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Endogenous levels of p53 were measured by immunoblotting, while residual cellular levels of p53 were quantitated by densitometry. The half-life of p53 was measured based on the decay of normalized (to Actin control) p53 levels to 50% of their original level. Values are an average of two independent experiments. (e) Hades-mediated degradation of p53 is recovered in the presence of leptomycin B (LMB). H1299 cells were cotransfected with 1 μg of each indicated plasmid. After 24 h, cells were treated with LMB (20 nM), for 4 h (lanes 3–6), and the level of p53 and GFP-Hades was measured by immunoblotting using anti-p53 and anti-GFP antibodies. An anti-Actin antibody was used as a loading control. (f) p53 stability in H1299 cells cotransfected with 0.5 μg wild-type or mutant (C135Y) p53 plasmid and the indicated amounts of GFP-Hades plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, ectopically expressed p53 and GFP-Hades were measured by immunoblotting. In addition, stability was determined as in (d). Values are the average of two independent experiments