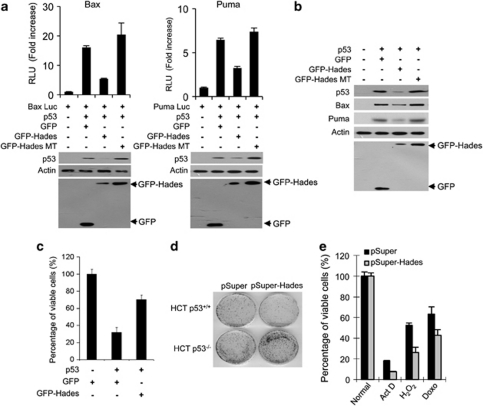
Figure 4.
Hades restores p53-dependent growth suppression. (a) Hades suppresses p53-dependent transcriptional activity. H1299 cells were cotransfected with reporter plasmid (Bax-luc or Puma-luc) and plasmids encoding p53, GFP, GFP-Hades, and GFP-Hades MT as indicated. At 24 h after transfection, the relative luciferase activities were measured. Also, the level of p53 proteins was measured using anti-p53 antibody. (b) Hades suppresses endogenous p53 downstream genes. H1299 cells were cotransfected with 1 μg plasmids encoding p53, together with expression plasmid of GFP, GFP-Hades, or GFP-Hades MT. At 24 h after transfection, the protein levels of Puma and Bax were analyzed by immunoblotting. (c) Hades inhibits p53-mediated growth suppression. MTS cell proliferation assays were performed in U2OS cells at 72 h after cotransfection with 1 μg plasmids encoding p53, GFP, GFP-Hades, and GFP-Hades MT as indicated. (d) Effect of Hades expression on the clonogenic growth of HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53−/− cells, as assessed by colony formation assays. Cells were cotransfected with 1 μg pSuper control plasmid or pSuper-Hades plasmid, further incubated in media containing G418 (500 μg/ml) for 14 days, and stained with crystal violet (0.05%). (e) Hades knockdown reduces cell viability under various stress conditions. Stable Hades-knockdown MCF7 cells (gray bar) and control MCF7 cells (black bar) were exposed to H2O2 (10 μM), actinomycin D (1 μM), or doxorubicin (500 nM) for 24 h, and cell viability was measured using the MTS assay. Error bars represent the means (S.E.M.) of at least three independent experiments