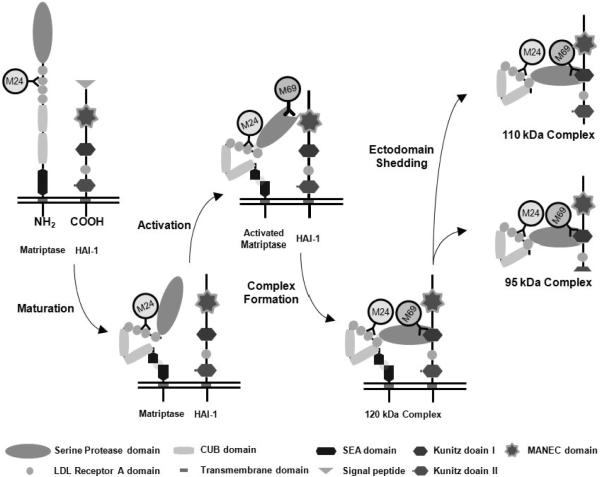
Figure 1. The matriptase-HAI-1 life cycle and the specificity of the various matriptase mAbs.
Both matriptase and HAI-1 are membrane-bound proteins with multiple distinct domains and modules, as indicated. Matriptase is synthesized as a full length zymogen which is rapidly converted into an activation-competent, mature form through a cleavage within the SEA domain (N-terminal process)26, 49. The signal peptide of HAI-1 is removed during the maturation process. Through autoactivation, latent matriptase is converted into active matriptase with full proteolytic activity. Active matriptase is rapidly inactivated by binding to its endogenous inhibitor HAI-1. Matriptase-HAI-1 complexes then are shed as complexes of two different sizes, depending on where the HAI-1 is cleaved. The mAb M24 recognizes a non-catalytic domain of matriptase, though the exact location of the epitope has not been determined. This matriptase mAb can detect both latent and activated forms of matriptase, as indicated. The mAb M69 recognizes an epitope on the serine protease domain that is only present in activated matriptase. This mAb is, therefore, able to distinguish activated matriptase from latent matriptase.