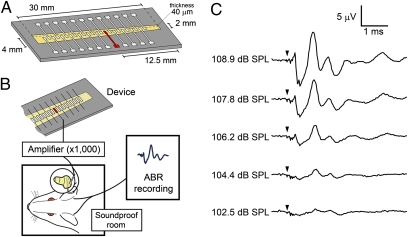
Fig. 2.
ABR recording using a prototype device. (A) Schematic drawing of a prototype device with a piezoelectric membrane (yellow). A piezoelectric membrane has a thickness of 40 μm and a length of 30 mm. An array of 24 electrodes, made of aluminum thin film, is fabricated on the upper side of a piezoelectric membrane, which is aligned in the midline of the trapezoidal slit of the stainless plate. An electrode used in the experiment of stimulating auditory primary neurons is located 12.5 mm from the shorter side of the trapezoidal membrane (shown in red). (B) Schematic drawing of a setting for ABR recording using a piezoelectric device. Electrical signals generated by a piezoelectric membrane in response to acoustic stimuli are amplified and transferred to the cochlea. Bioelectrical signals were recorded as ABRs from needle electrodes inserted dorsal to ears. (C) ABRs by electrical signals derived from a prototype device by acoustic stimuli. Arrowheads indicate the timing of acoustic stimuli.