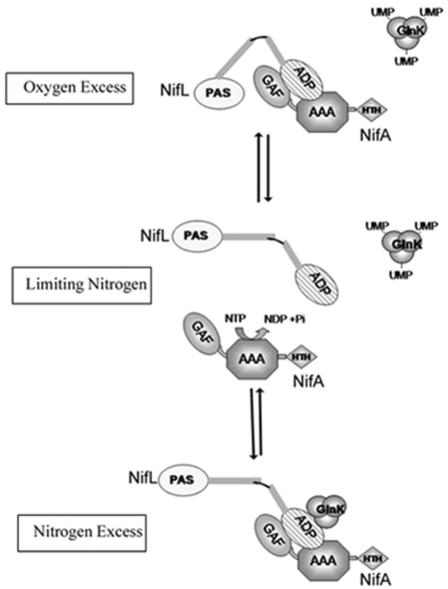
FIG. 4.
Model showing potential interactions between Av NifL and Av NifA in response to environmental cues. Only the PAS1 and ADP binding domains of NifL are shown (open and cross-hatched ovals, respectively). The three domains of Av NifA are labeled GAF, AAA, and HTH. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions GlnK is uridylylated, and provided that the flavin moiety in Av NifL is reduced, Av NifA is free to activate transcription, catalyzed by ATP hydrolysis (center diagram). However, when Av NifL is oxidized, the NifL-NifA binary complex is formed, perhaps promoted by conformational changes mediated via the PAS domain. Formation of the complex sequesters Av NifA, preventing transcriptional activation. Under nitrogen-excess conditions, when GlnK is in the noncovalently modified form, it interacts with the C-terminal ADP binding domain of Av NifL to promote formation of a ternary complex in which the activity of Av NifA is also inhibited.