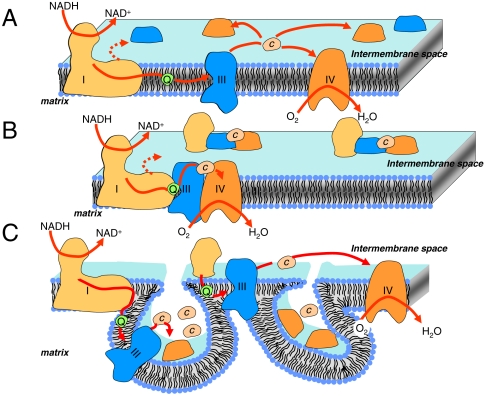
Fig. P1.
Mitochondrial respiration involves electron transfer from NADH to molecular oxygen. This overall reaction is mediated by membrane-embedded proteins (here depicted as complex I, complex III, and complex IV); quinones (in green), which are membrane soluble and transfer electrons between complexes I and III; and cytochrome c, which is soluble in the intermembrane space and transfers electrons between complexes III and IV. In A is shown the “liquid model” in which soluble electron carriers freely diffuse between the membrane-embedded complexes. In B are shown “respirasomes” or the solid-state model, in which the membrane complexes are assembled within supramolecular edifices that trap the soluble electron carriers and thereby restrict their diffusion. In C is shown the compartmented model, in which the intricate folding of the inner membrane defines local compartments that allow the free diffusion of cytochrome c but prevent equilibration between compartments.