Figure 3. Mechanisms of lncRNA function.
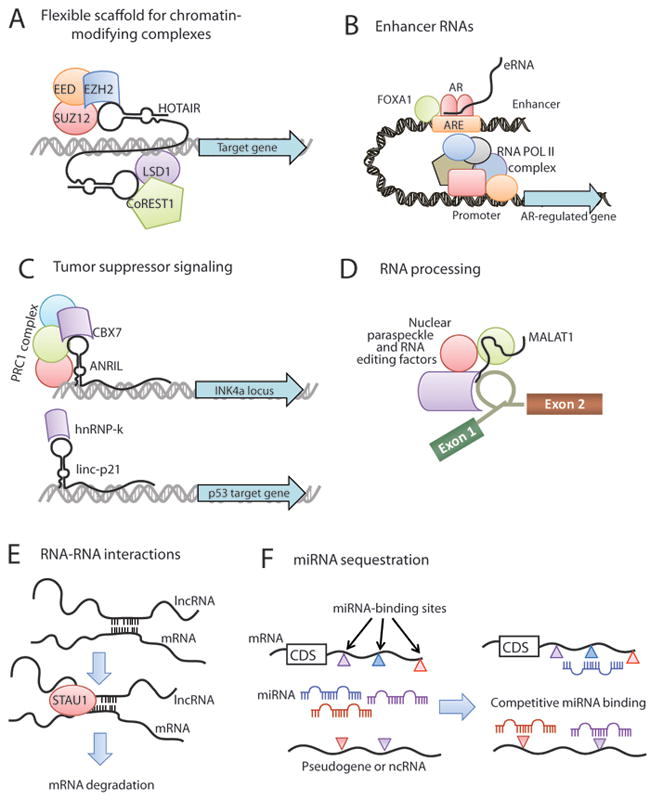
(A) lncRNAs, such as HOTAIR, may serve as a scaffolding base for the coordination of epigenetic or histone-modifying complexes, including Polycomb repressive complexes and LSD1/CoREST. (B) Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) transcribed from gene enhancers may facilitate hormone signaling by cooperating with lineage-specific complexes such as FOXA1 and Androgen Receptor. (C) lncRNAs may directly impact tumor suppressor signaling either by transcriptional regulation of tumor suppressor genes through epigenetic silencing (e.g. ANRIL, upper) or by mediating activation of tumor suppressor target genes (e.g. linc-p21, lower). (D) MALAT1 and NEAT2 lncRNAs may be integral components of the nuclear paraspeckle and contribute to post-transcriptional processing of mRNAs. (E) Gene expression regulation may occur through direct lncRNA-mRNA interactions which arise from hybridization of homologous sequences and can serve as a signaling for STAU1-mediated degradation of the mRNA. (F) RNA molecules, including mRNAs, pseudogenes, and ncRNAs, can serve as molecular sponges for miRNAs. This generates an environment of competitive binding of miRNAs to achieve gene expression control based upon the degree of miRNA binding to each transcript. The colored triangles represent different miRNA binding sites in a transcript. Abbreviation: CDS, coding sequence.
