Figure 4. Clinical implications of lncRNAs.
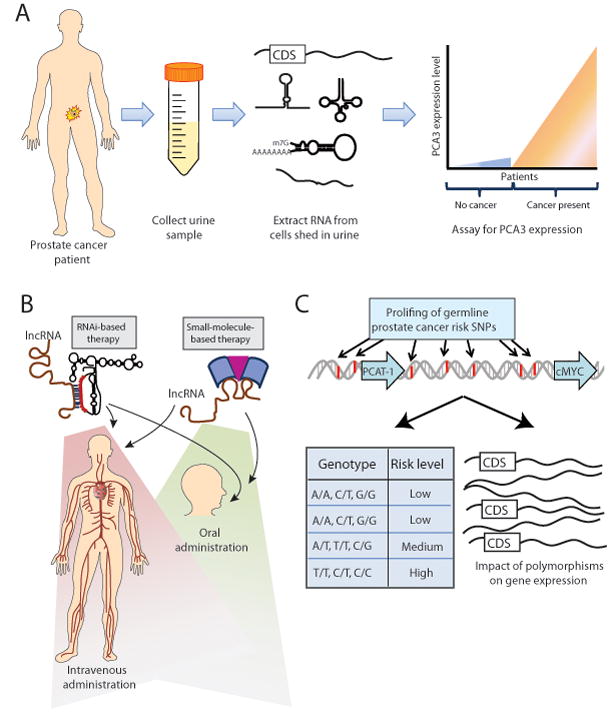
(A) The PCA3 urine biomarker test for prostate cancer employs a non-invasive approach to disease diagnosis by collecting patient urine samples, isolating nucleic acids from cells in the urine sediment, and quantifying PCA3 expression. (B) lncRNA-based therapies may target the lncRNA by utilizing either RNA interference (RNAi), which uses sequence homology between the lncRNA and the RNAi therapeutic molecule, or a small molecule therapy that interacts with the lncRNA. These therapeutic avenues may be appropriate for systemic therapy by either intravenous or oral administration. (C) Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) may provide germline polymorphisms that predict an individual patient’s clinical risk for disease development, response to therapy, or disease aggressiveness, while also providing molecular information through the impact of polymorphisms on gene expression of key genes. Abbreviation: CDS, coding sequence.
